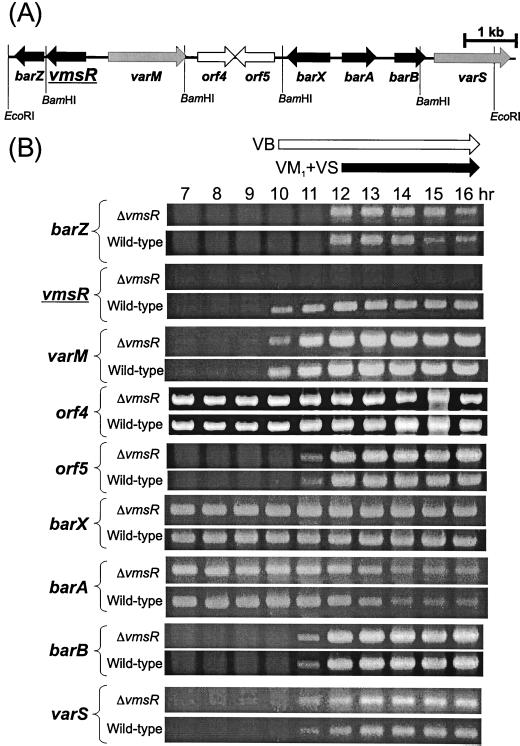
FIG. 3.
(A) Gene organization in the 10-kbp region containing the vmsR gene in S. virginiae. Solid arrows, gray arrows, and open arrows indicate regulator genes, resistance genes for VM, and genes of unknown function, respectively. (B) Transcriptional comparison of vmsR-surrounding genes in the vmsR disruptant and the wild-type strain by RT-PCR. RT-PCR conditions were previously described (8). Production of VB and VM1 plus VS is indicated by open and solid arrows, respectively. With the entire sample, RT-PCR was carried out without reverse transcriptase to confirm that the signals shown were derived from mRNA and not from contaminating genomic DNA. ΔvmsR, vmsR disruptant; Wild-type, S. virginiae MAFF 10-06014.