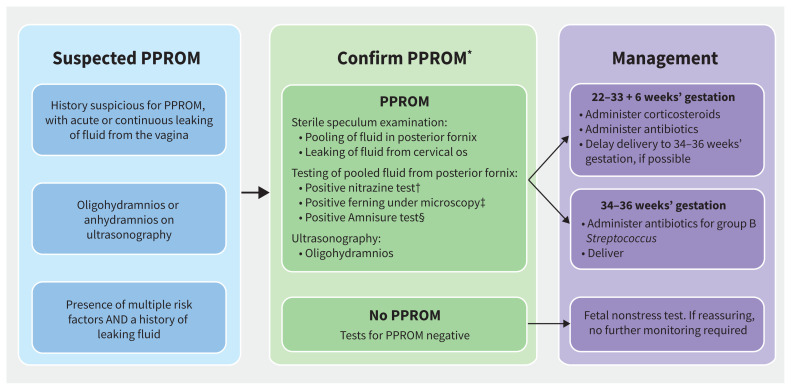
Figure 2:
Algorithm for the confirmation of preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM) and its management, according to gestational age. Risk factors for PPROM are listed in Appendix 1, Supplemental Table 1, available at https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.212068/tab-related-content. *Not all tests are required for diagnosis of PPROM. Large-volume pooling or visualization of fluid leaking from the os, as well as a positive Amnnisure test, may be diagnostic on their own. Presence of ferning may be diagnostic alone, but is more reliable in combination with another test. Nitrazine is a nonspecific pH test of the pooled fluid in the posterior fornix obtained during a sterile speculum examination, and is not a reliable indicator alone. †Normal vaginal pH is 4.5–6.0 and amniotic fluid has a pH of 7.1–7.3. Nitrazine paper will turn from yellow to blue when a sample has a pH greater than 6.5.2 ‡Obtain a sample of pooled fluid in the posterior fornix on speculum examination and let it dry on a glass slide. With inspection under a microscope, a ferning pattern will be seen if the sample contains amniotic fluid.2 §Amnisure is a commercial test for samples of pooled fluid from the posterior fornix to indicate rupture of membranes based on detection of placental α-microglobulin (PAMGG-1).2