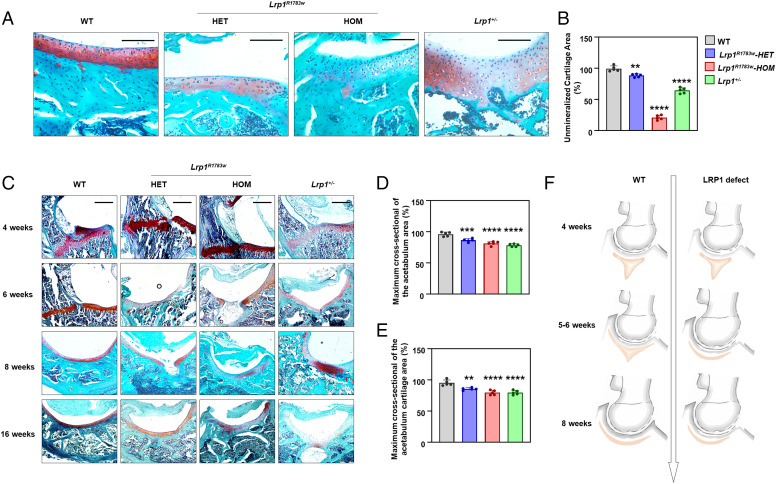
Fig. 2.
Histology of the hip joints of heterozygous and homozygous Lrp1 R1783W mice, Lrp1+/− mice, and their WT littermates. (A) Sections of mice acetabulum cartilage at 40x magnification at 8 wk. Scale bar: 100 μm. Lrp1R1783W and Lrp1+/− mice showed sparser acetabulum cartilage compared with WT mice. (B) The unmineralized cartilage area calculated using the contrast red-green feature. Values = means ± SD; *P < 0.01; **P < 0.0001. The area of WT mice was significantly larger than those of Lrp1 R1783W and Lrp1+/− mice. (C) Sections in 10x magnification at 4, 6, 8, and 16 wk. Scale bar: 200 μm. The triradiate cartilage had closed completely before 6 wk in KI and KO mice, while it closed after 8 wk in WT mice. The quantitative results of maximum cross-sectional of the actabulum area (D) and maximum cross-sectional of the acetabulum cartilage area (E) was shown. (F) Schematic of the LRP1-deficient hip joint. Premature fusion of the triradiate cartilage (red) causes dysplasia of the hip.