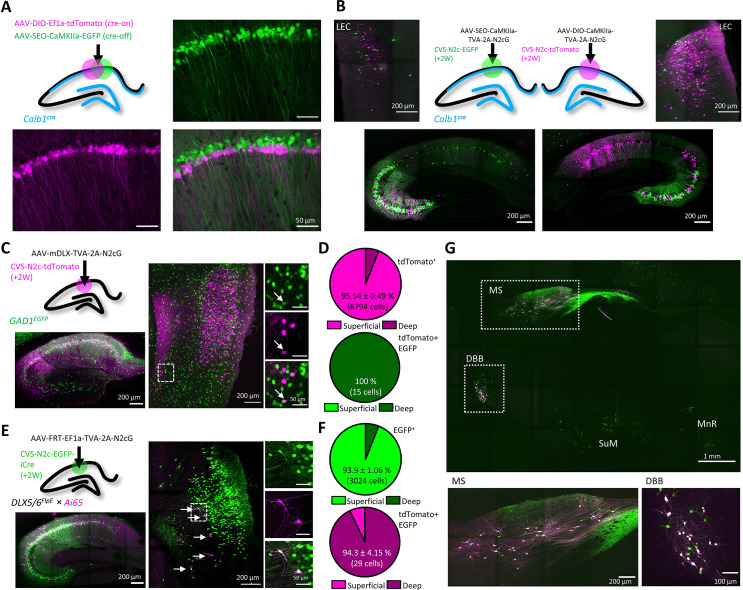
Figure 5. An AAV vector suite for targeting multiple and diverse neuronal populations.
(A) Graphical representation (top left) and representative confocal images, demonstrating differential targeting of superficial and deep CA1 pyramidal neurons using a combination of cre-on and cre-off AAV vectors. (B) Graphical representation (top center) for dual retrograde labeling from superficial (bottom left, green) and deep (bottom right, magenta) CA1 pyramidal neurons and the resulting distribution pattern of their corresponding projection neurons in the EC (top left and top right). (C) Graphical representation of the viral injection scheme for mapping inputs into hippocampal inhibitory neurons (top left), and representative parasagittal images of labeled cells in the HC (bottom left) and LEC (right). Expanded images show a double-labeled neuron in EC-6. (D) Distribution of all retrogradely labeled cells (top) and of double-labeled cells only (bottom) among the superficial layers 2 and 3 and the deep layers 5 and 6 of the LEC. N=8 sections/3 animals. (E) Same as (C), but for Dlx5/6FlpE × Ai65 mice. (F) Same as (D) for the experiments described in (E). N=8 sections/3 animals. (G), A representative parasagittal image of deep brain structures following the injection scheme described in (E). SuM – Supramammilary Nucleus; MnR – Median nucleus Raphe.