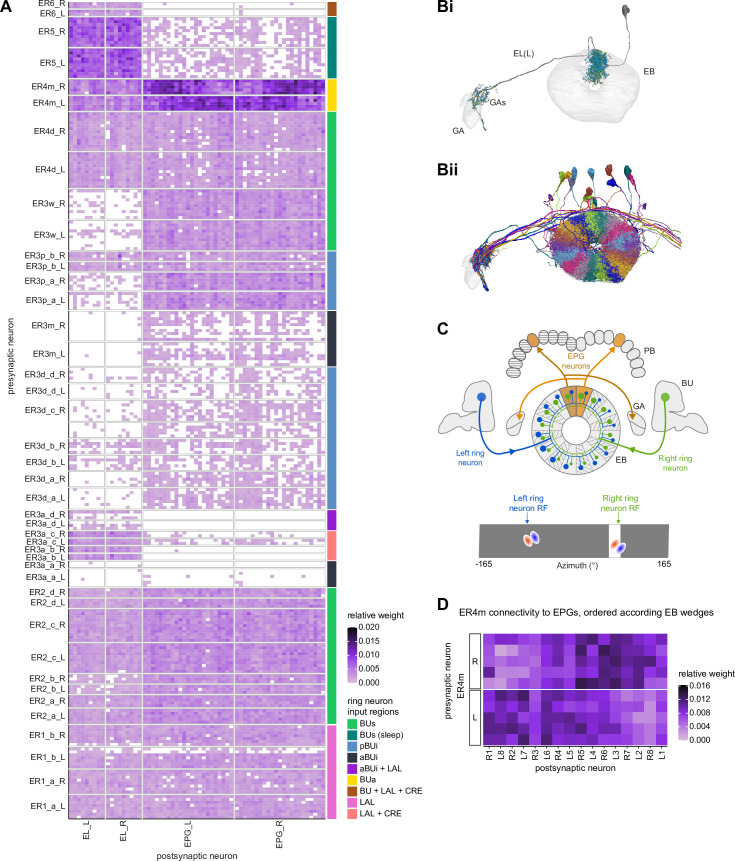
Figure 11. Ring neuron to columnar connectivity.
(A) Neuron-to-neuron connectivity matrix for connections from ring neurons to EL and EPG neurons in the ellipsoid body (EB) on a single neuron level. The boxes on the right side are colored according to the ring neuron’s input region. (B) Morphological renderings of EL neurons and renderings of innervated regions of interest (ROIs). Note that EL neurons target a small region next to the GA, called the gall surround (GAs). (Bi). Single left hemisphere EL neuron with blue dots marking the location of postsynaptic sites and yellow dots those of presynaptic sites. (Bii). Full population of EL neurons. (C) Schematic illustrating variation in synaptic strength in ring neuron to EPG connections due to neural plasticity. Top: connectivity between ring neurons and EPG neurons. Bottom. Illustration of receptive fields (RFs) of single-ring neurons. (D) Connectivity matrix of ER4m inputs to EPG neurons that have been sorted and averaged according to the EB wedge they innervate.