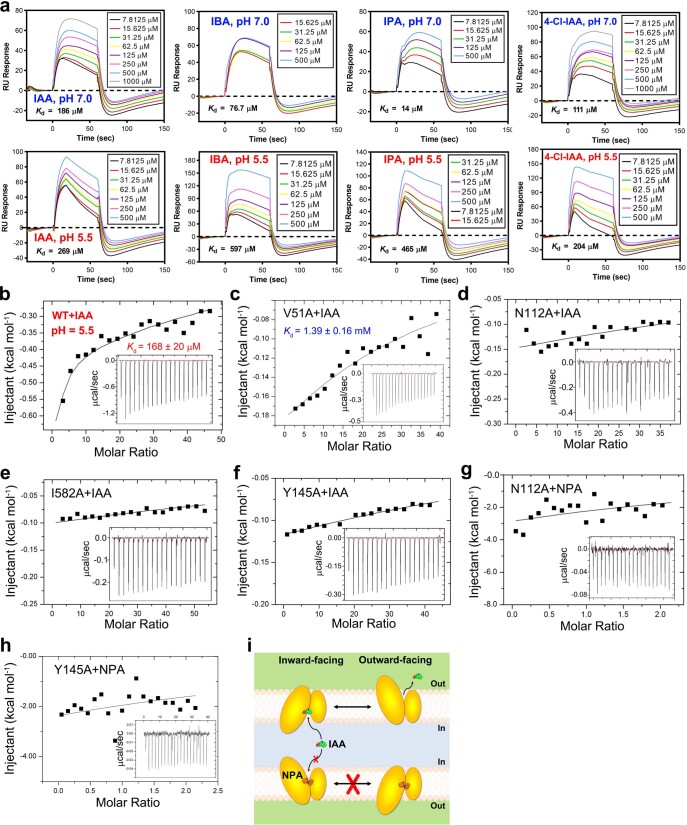
Extended Data Fig. 7. Binding between PIN1 and IAA, NPA or other natural auxins.
a, The binding affinity between PIN1 and IBA, IPA, or 4-Cl-IAA under pH 7.0 or 5.5 as examined by SPR, respectively. Under acidic pH, the binding affinities decreased dramatically for IBA and IPA, while for 4-Cl-IAA, the Kd had an about two-fold increase. These results suggest that PINs can bind range of natural auxins but whether PIN1 can transport these auxins awaits further studies. b, IAA-ITC results for the WT PIN1 at pH 5.5. c–f, IAA-ITC results for the PIN1 V51A, N112A, I582A and Y145A mutants at pH 7.0, respectively. No apparent binding are derived for the N112A, I582A and Y145A mutants. For V51A, the fitted binding affinity is 1.39 ± 0.16 mM, 17-fold higher than that of the WT PIN1. g, h, NPA-ITC results for the PIN1 N112A and Y145A mutants. i, Cartoon model for the alternating access mechanism of IAA transport by PIN1 and inhibition by NPA.