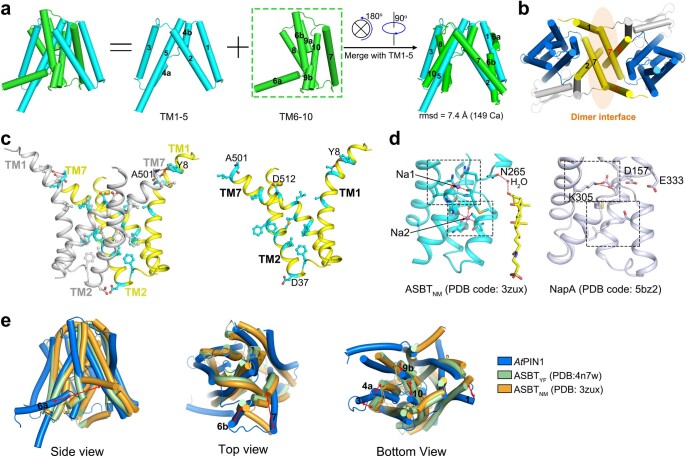
Extended Data Fig. 5. PIN1 shares a NhaA-fold.
a, The first and last five TMs of PIN1 are structurally inverted repeats. TM6-10 merges well with TM1-5 by two rotational operations as indicated. b, The dimer interface of PIN1 is formed by TM1, 2, 7 of each monomer. c, The dimer interface mainly consists of hydrophobic residues. d, Two sodium binding sites of ASBTNM (left) and the corresponding positions in the Na+/H+ transporter NapA (right). Left, the sodium ions are shown in purple spheres. N265 and the substrate taurocholate are shown in sticks. The water molecule mediating the interaction between N265 and taurocholate is shown in a red sphere. Right, a lysine residue is present in the Na1 site in NapA and stabilizes the crossover helices through ionic interactions. The Na2 site of NapA is composed of mainly hydrophobic residues as shown in sticks. e, Structural alignments between PIN1 and the inward-facing structures of ASBTYF (PDB code: 4N7W) and ASBTNM (PDB code: 3ZUX).