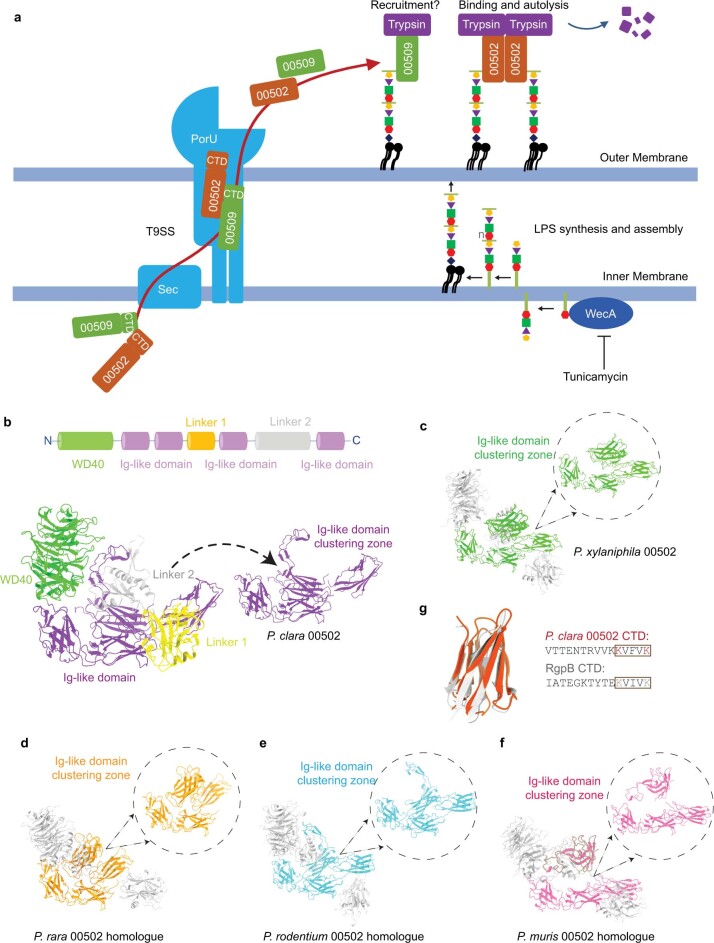
Extended Data Fig. 8. Model of Paraprevotella-mediated trypsin degradation and structural predictions of 00502.
a, Model of Paraprevotella-mediated trypsin degradation: 00502 and 00509 proteins are transported across the outer membrane of Paraprevotella via the Type IX secretion system (T9SS). PorU is an essential T9SS component that cleaves the C-terminal domain (CTD) of T9SS-dependent proteins and anchors the proteins to Paraprevotella LPS molecules. WecA mediates the initial step of LPS O-glycan synthesis, and disruption of WecA function (e.g., with tunicamycin treatment) causes release of T9SS-dependent proteins. 00502 acts as a core effector component, facilitating trypsin association and auto-degradation possibly mediated by 00502 oligomerization, whereas 00509 may play a supporting and dispensable role in facilitating trypsin recruitment. Sec: Sec system that exports proteins across the cytoplasmic membrane. b, AlphaFold2-based structural prediction of P. clara 00502 protein with individual domains highlighted. Four out of the five Ig-like domains are shown; the last Ig-like domain that serves as the T9SS C-terminal target domain therefore does not form part of the Ig-like domain clustering zone is omitted here (shown separately in panel g). c–f, AlphaFold2-based structural prediction of P. xylaniphila, P. rara, P. rodentium and P. muris 00502 homologues with the conserved Ig-like domain clustering zone highlighted. g, Alignment of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of P. clara 00502 with that of Porphyromonas gingivalis RgpB protein. The “KXXXK” motif is a signature of T9SS C-terminal target domain-containing proteins.