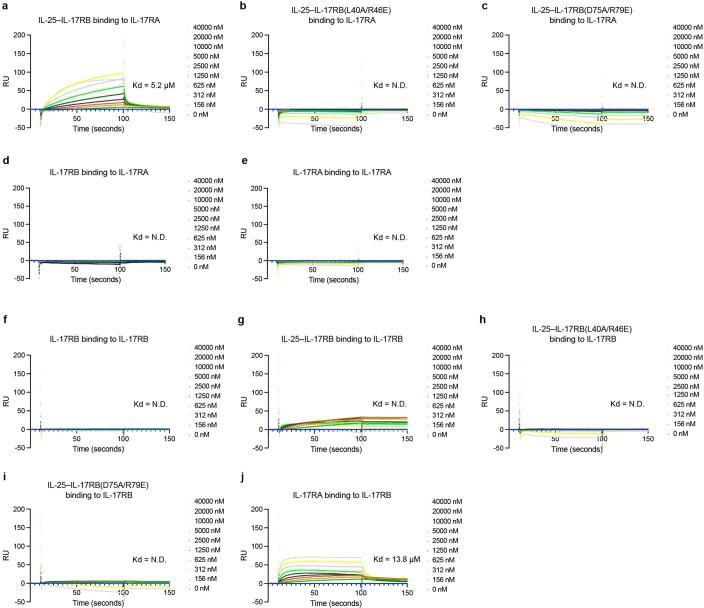
Extended Data Fig. 6. Supporting surface plasmon resonance (SPR) binding data for IL-25, IL-17RB, and IL-17RA interactions.
a, sensorgram showing wt IL-25–IL-17RB complex binding to immobilized IL-17RA. b, sensorgram showing no binding of IL-25–IL-17RB(L40A/R46E) mutant complex to immobilized IL-17RA. c, sensorgram showing no binding of IL-25–IL-17RB(D75A/R79E) mutant complex to immobilized IL-17RA. d, sensorgram showing no binding of IL-17RB to immobilized IL-17RA. e, sensorgram showing no binding of IL-17RA to immobilized IL-17RA. f, sensorgram showing no binding of IL-17RB to immobilized IL-17RB. g, sensorgram showing wt IL-25–IL-17RB complex binding to immobilized IL-17RB. h, sensorgram showing no binding of IL-25–IL-17RB(L40A/R46E) mutant complex to immobilized IL-17RB. i, sensorgram showing no binding of IL-25–IL-17RB(D75A/R79E) mutant complex to immobilized IL-17RB. j, sensorgram showing weak binding of IL-17RA to immobilized IL-17RB. Analyte concentration ranges are shown next to each sensorgram. Dissociation constants (Kd) are indicated on the sensorgrams. N.D. = Not Determined. Single experiments (n = 1) were performed for b, c, and e–j. Sensorgrams for a and d are representative of a single experiment from two independent experiments (n = 2).