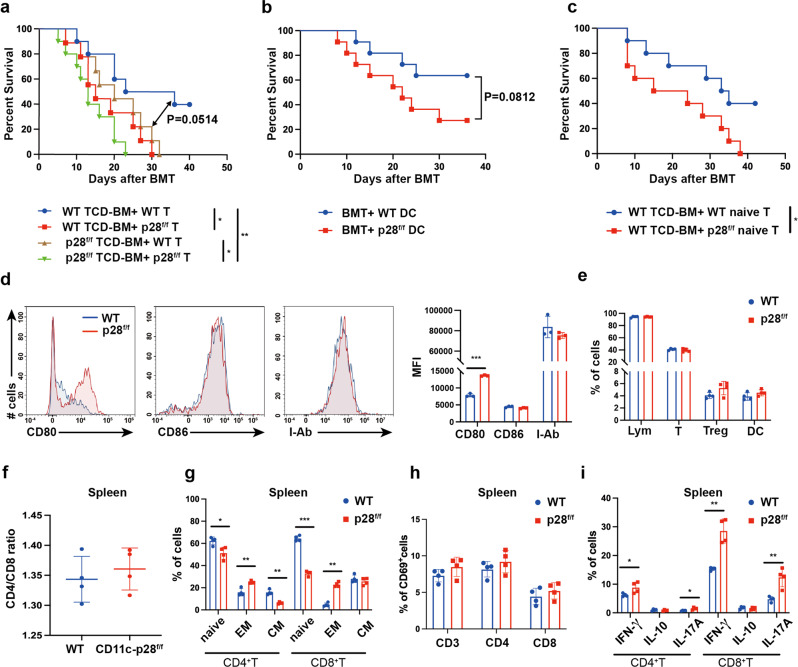
Fig. 3.
Donor DC-derived IL-27 p28 deficiency and intrinsic functional defects of T cells are both responsible for exacerbated aGVHD. a BALB/c recipients received either WT or CD11c-p28f/f allografts of 5 × 106 TCD-BMs and 1 × 106 T cells as indicated (n = 10 per group). b WW recipients were injected with either 1 × 106 WT DCs or CD11c-p28f/f DCs at day 0, day1, and day2 post-BMT (n = 10 per group). The overall survival curve is depicted. c BALB/c recipients received 5 × 106 TCD-BMs from WT mice together with 1 × 106 naive T cells from WT or CD11c-p28f/f mice, respectively (n = 10 per group). d–i Splenocytes from normal donors were detected by flow cytometry. d CD80, CD86, and MHC-II expression on DCs. e Percentages of lymphocytes, CD3+ T, Tregs, and DCs. f The ratio of T cells in the spleen. g Percentages of T cell suesets. h CD69 expression on T cells. i IFN-γ, IL-17A, and IL-10 expression in T cells (n = 4 per group). Data are representative of three independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001