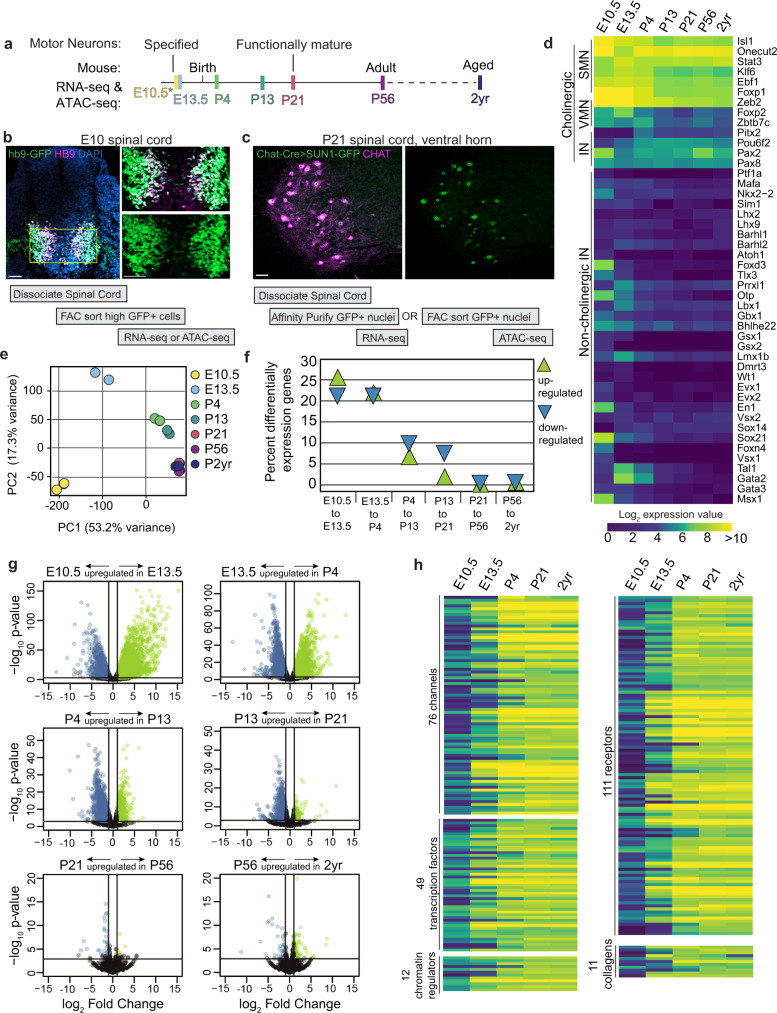
Fig. 1. Motor neuron gene expression is dynamic during embryonic and early postnatal ages.
a Timeline of motor neuron development and functional maturation in mice. b A spinal cord section from an Hb9-GFP transgenic E10 embryo and outline of the procedure used to isolate motor neurons. Immunostaining shows co-labeling of HB9 protein (magenta) with high GFP expression from the transgene (green). The boxed region from the left image is shown with split colors on the right. c The right ventral horn region of a P21 Chat-Cre; Sun1-GFP spinal cord section and outline of the procedure used to isolate motor neuron nuclei at all ages from E13.5 to 2 years. Immunostaining shows co-labeling of CHAT protein (magenta) with SUN1-GFP (green). d Expression of transcription factors that mark cholinergic skeletal motor neuron (SMN), visceral motor neurons (VMN), interneurons (IN), and non-cholinergic cell types in the spinal cord at all profiled ages. A handful of VMN and IN markers are also expressed in SMNs, as seen in Supplementary Fig. 2f. e Principal component analysis on RNA-seq data at all timepoints. Circles of the same color represent biological replicates for each timepoint. f Percent of expressed genes that are upregulated or downregulated between two consecutive timepoints. This plot is a summary of the differential gene expression plots in (g). g Plots showing differential gene expression between consecutive timepoints. Each dot represents one gene, colored dots are genes that are upregulated (green) or downregulated (blue) at least 2-fold with a p value <0.001. h Expression trajectories of various categories of functional genes. The scale for the heatmap is the same as in d. All scale bars are 50 μm.