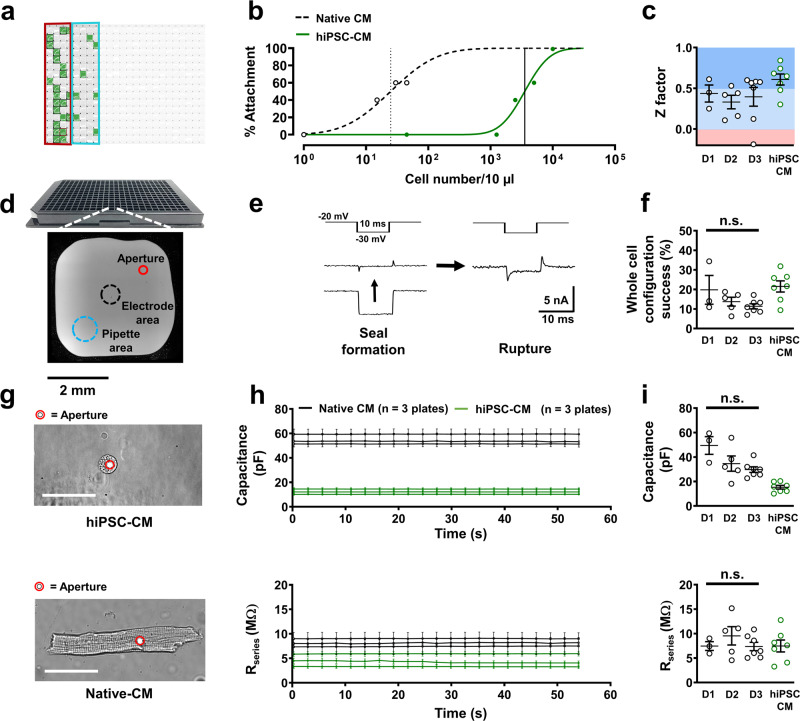
Fig. 2. Quality control of automated patch-clamp of native atrial and ventricular cardiomyocytes (Native CM).
a Representative 384-well APC chip partially filled with native CMs is shown as a screenshot of Nanion DataControl 384 software with unused areas shaded out. Green boxes represent successful whole-cell configuration during L-type calcium current (ICa,L) measurement. Red and blue rings indicate atrial and ventricular CM partitions respectively. b Cellular density-dependent optical attachment rates of native ventricular cardiomyocytes and human ventricular induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CM) onto the patch-clamp aperture. c Z factor analysis of individual runs for assessment of reproducibility (ICa,L currents) over three separate experimental days (D1, D2, D3) and therefore three animals. d NPC-384T chip with a photomicrograph of a single well with locations of interest labeled. e Representative membrane resistance during seal formation and membrane rupture of a native CM in the presence of a membrane test pulse. f Percentage success rates for whole-cell configuration from single plates of native CMs over three separate experimental days and hiPSC-CMs used in this protocol during ICa,L acquisition. P = 0.210 g Photomicrograph of an attached ventricular hiPSC-CM and ventricular native CM. The patch-clamp aperture is obscured by the cell. Scale bar denotes 50 µm. h Time course of membrane capacitance and series resistance (Rseries) in hiPSC-CMs (3 plates, same day) and native CMs (3 plates, same day) over successive ICa,L experiments. i Cellular capacitance (P = 0.054) and Rseries (P = 0.871) averages from single plates over three separate experimental days. Data are mean ± SEM. n = mean of 24 wells (b) or single plates (c, f, h, i).