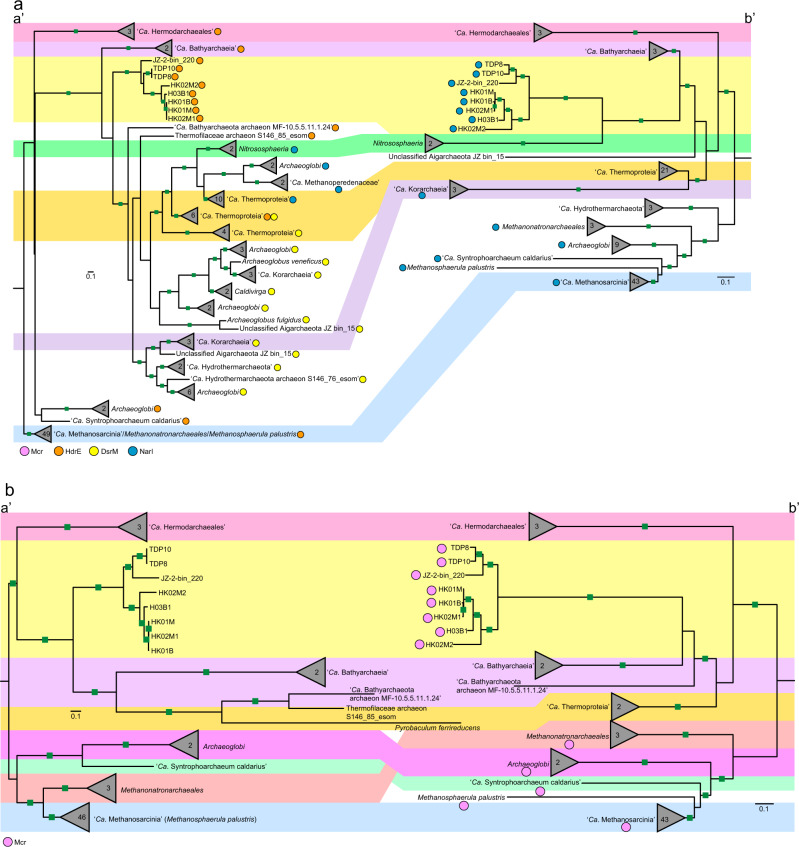
Fig. 5. Phylogeny of NarI-domain-containing b-type cytochromes and concatenated HdrDE complexes in archaea.
a Phylogeny of NarI-domain-containing b-type cytochromes in archaea. b Phylogeny of concatenated HdrDE complexes in archaea. The maximum-likelihood trees of NarI-domain-containing b-type cytochromes (a (a’)) and concatenated HdrDE subunits (b (a’)) from representative archaea are inferred with IQ-TREE (LG + C60 + F + G, -bb: 10,000 for NarI-domain, 1000 for HdrDE). The b-type cytochromes comprising different enzyme complexes are indicated by different color dots (light red for HdrE, yellow for DsrM, and blue for NarI). HdrE heterodisulfide reductase E subunit, DsrM sulfite reductase M subunit, NarI dissimilatory nitrate reductase I subunit. The maximum-likelihood trees of a concatenated set of 122 archaeal-specific marker proteins using the same genomes as those of NarI-domain-containing b-type cytochrome tree (a (b’)) and HdrDE complexe tree (b (b’)), respectively. The trees were computed with IQ-TREE using LG + C60 + F + G model. These genomes or clades with Mcr complexes are marked by pink dots. The bootstrap support values ≥95 are indicated with green filled squares.