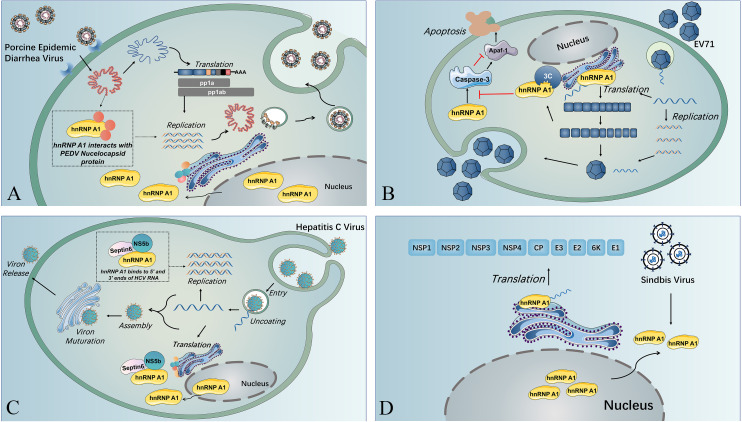
Figure 2.
The multiple functions of hnRNP A1 in viral life cycles. (A) Nuclear translocation of SV induces cytoplasmic retention of hnRNP A1, and hnRNP A1 binds to the 5’ UTR of SV RNA, resulting in enhanced viral translation. (B) HnRNP A1 interacts with the nucleocapsid of PEDV and facilitates PEDV replication near the nucleus. (C) HnRNP A1 binding to the 5’ UTR and 3’ UTR of HCV RNA and forming a complex with septin 6 and NSb5 induces the cyclization of HCV RNA and reinforces HCV RNA replication. (D) HnRNP A1 could bind to Apaf-1 mRNA to promote Apaf-1 translation and then upregulate the expression of caspase-3, resulting in cell apoptosis and virion release. EV71 3C protease could splice hnRNP A1 and abolish its capacity to bind to Apaf-1 mRNA and downregulate caspase-3 expression, guaranteeing sufficient virus replication before virion release.