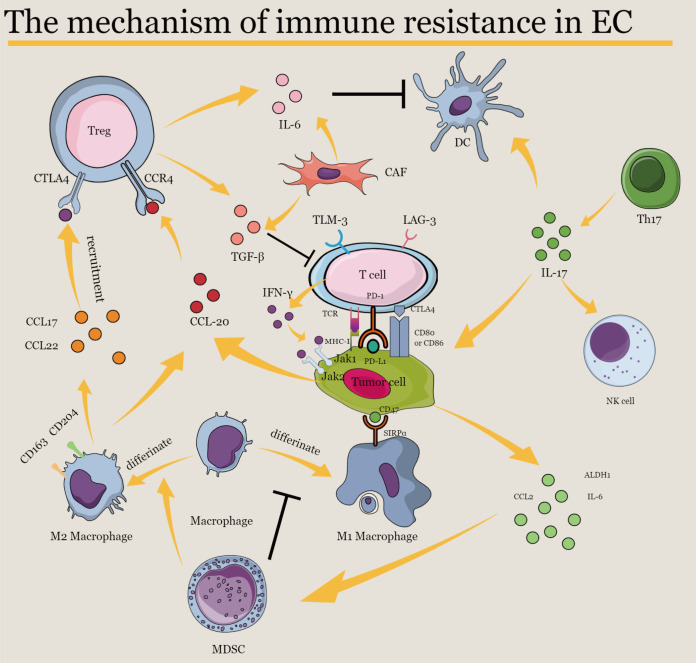
Figure 2.
The mechanism of immune resistance in EC. IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-17, interleukin-17; PD-1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD-L1, programmed cell death ligand 1; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein 4; CCR4, C–C chemokine receptor type 4; CCL2, C–C motif ligand 2; CCL17, C–C motif ligand 17; CCL20, C–C motif ligand 20; CCL22, C–C motif ligand 22; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TIM-3, T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3; LAG-3, lymphocyte-activation gene 3; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; MHC-I, major histocompatibility complex class I; ALDH-1, aldehyde dehydrogenase 1; SIRPα, signal regulatory protein alpha; JAK1, Janus kinase 1; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; Treg, regulatory T cell; CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; DC, dendritic cell; NK, natural killer; Th17, T helper 17; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell.