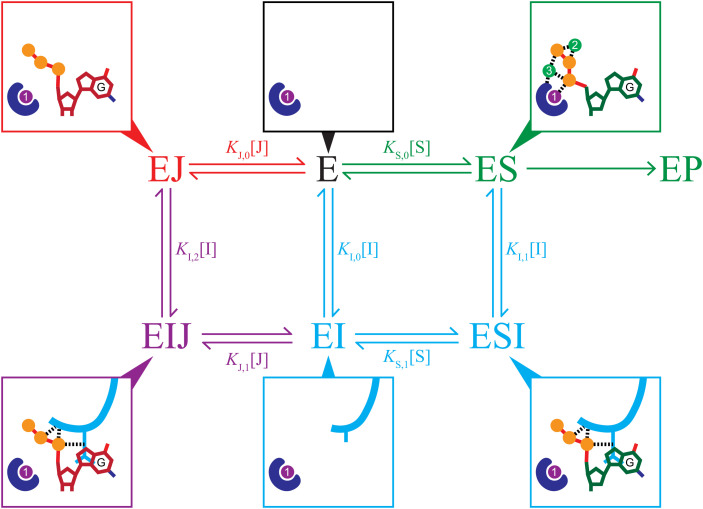
Fig. 7.
An inhibition scheme combining a mixed-type inhibitor (I = Gp1.2, cyan) with a competitive inhibitor (J = GTP, red). The blue shape represents the active-site HD motif, and the purple and green circles are the proposed catalytic metal ions (SI Appendix, Fig. S5) (20). Product release and any possible conformational change steps are excluded for simplicity. The surrounding boxes show minimal schematics of the active site in the various states of the scheme with or without Gp1.2 (cyan), dGTP (green carbons), or GTP (red carbons). In a mixed-type inhibition scheme (cyan), inhibitor (I) binds to either E or ES, yielding inhibited complexes (EI or ESI) that prevent turnover to product (P). The increasing KM observed in Fig. 6C indicates a competitive-like mixed-type inhibition, wherein the inhibitor binds more tightly to E (i.e., KI,0 < KI,1). In a competitive inhibition scheme (red), inhibitor (J) binds only to E and prevents it from binding to substrate (S), therefore preventing turnover to product (P). Because Gp1.2 and GTP use different inhibition modes and form productive interactions in a ternary complex with Dgt (EIJ, purple), inhibition by both is combinatorial.