Fig. 1.
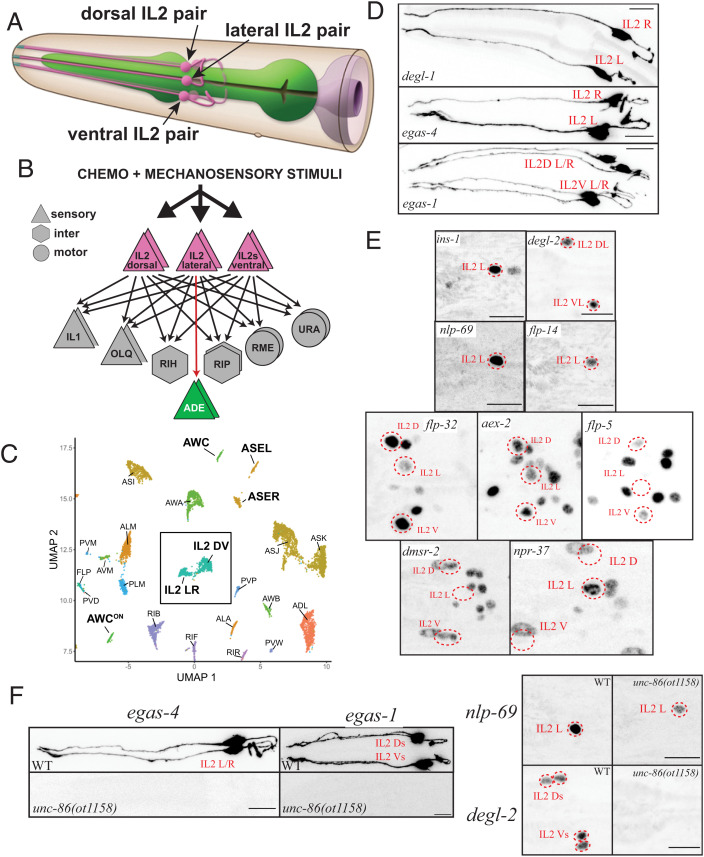
IL2 neurons are composed of distinct subclasses, all specified by the unc-86 terminal selector. (A) Schematic drawing of IL2 neurons, based on electron microscopical reconstruction (10). Reproduced with permission from ref. 58. (B) Synaptic connectivity of IL2 neurons. Data extracted from refs. 10 and 59. (C) Single cell transcriptome analysis showing similarity and differences among IL2 neuron subtypes, relative to other neuron classes. Reproduced from ref. 11. (D and E) Expression pattern analysis using reporter alleles or reporter transgenes support IL2 subtype classification. (D) Subtype-specific, cytoplasmically localized gfp promoter fusions expressed from integrated transgenes that show expression in the lateral IL2 subtype (degl-1: otIs825, egas-4: otIs833), or the dorsoventral IL2 subtype (egas-1: otIs846). (E) Nuclear-localized reporter alleles for subtype-specific markers. Lateral IL2 subtype: ins-1(syb5452[ins-1::SL2::gfp::H2B]), flp-14(syb3323[flp-14::T2A::3xNLS::gfp]), nlp-69(syb4512[nlp-69::SL2::gfp::H2B]), and npr-37(syb4440[npr-37::SL2::gfp::H2B]). Dorsoventral IL2 subtype: degl-2(syb5229[degl-2::SL2::gfp::H2B]), flp-32(syb4374[flp-32::SL2::gfp::H2B]), aex-2(syb4447[aex-2::SL2::gfp::H2B]), flp-5(syb4513syb4513[flp-5::SL2::gfp::H2B]), and dmsr-2(syb4514 [dmsr-2::SL2::gfp::H2B]). For several of the more broadly expressed markers, NeuroPAL was used for cell identification (ID) (images in SI Appendix, Fig. S2A). (F) IL2 subtype marker genes are unc-86 dependent. In an unc-86(ot1158) null allele, both lateral IL2 markers [nlp-69(syb4512) and egas-4/otIs833), and dorsoventral IL2 markers [degl-2(syb5229), egas-1/otIs846, flp-32(syb4374), and flp-5(syb4513)] are affected. Quantification is in SI Appendix, Fig. S2B. Images and quantification for flp-32 and flp-5 regulation by unc-86 are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S2 C and D.