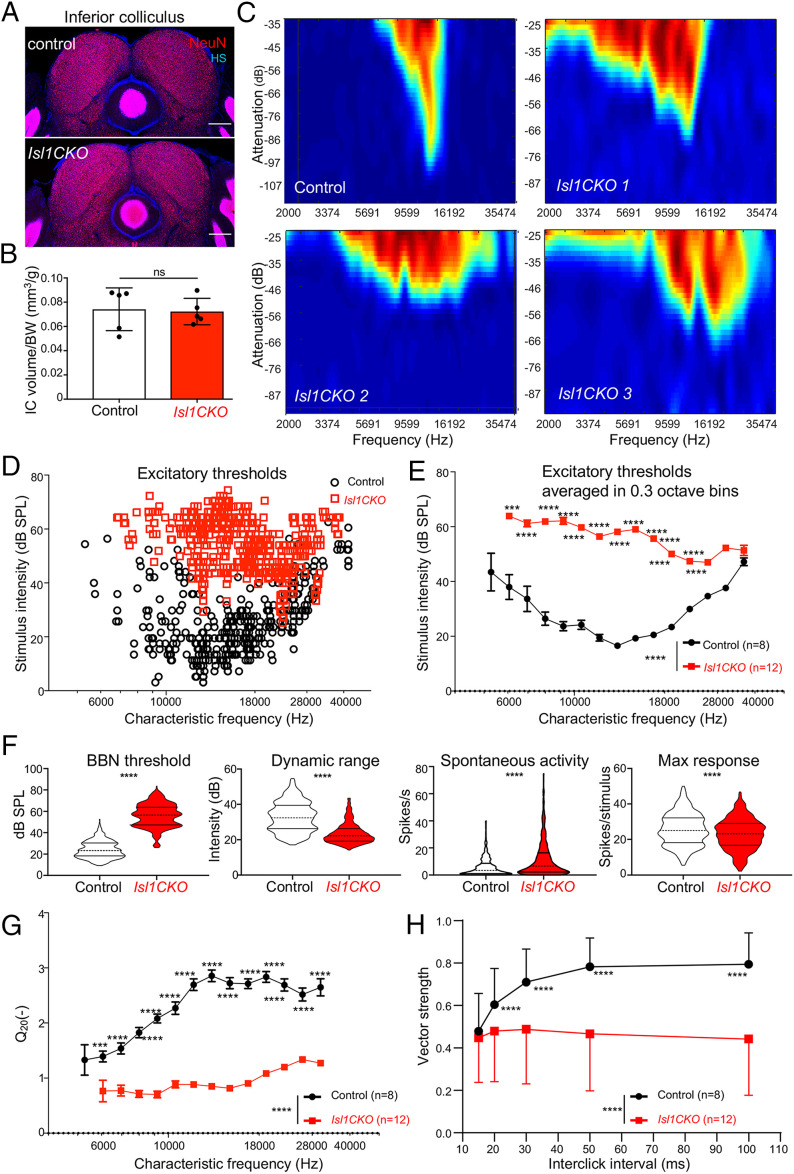
Fig. 6.
Characteristics of IC neurons (units) are affected in Isl1CKO mice. (A) Immunostaining of coronal brain sections for NeuN and nuclear staining Hoechst (HS). (Scale bars, 200 µm.) (B) Quantification of the adult control volume and Isl1CKO IC adjusted to body weight. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 5 mice per genotype), unpaired t test (ns, not significant). (C) Representative examples of tuning curves recorded in the IC display impairments in tuning properties with broad and irregular receptive fields in Isl1CKO compared to control mice. (D) Scatter diagram shows the distribution of the excitatory thresholds of IC neurons in dependency on the CF recorded in control and Isl1CKO mice. Note, no IC neurons are recorded below 6 kHz in Isl1CKO. (E) Excitatory thresholds of the IC neurons at different CFs are shown as averages in 0.3-octave bins in control and Isl1CKO mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. (F) Comparison of the rate intensity function parameters between control (n = 8) and Isl1CKO mice (n = 12): BBN threshold, dynamic range, spontaneous activity, and maximum response magnitude. Violin plots indicate median (middle line), 25th, and 75th percentile (dotted lines), unpaired t-test, ****P < 0.0001. (G) The sharpness of the neuronal tuning expressed by quality factor Q20 (the ratio between the CF and bandwidth at 20 dB above the minimum threshold) averaged in 0.3-octave bins is decreased in Isl1CKO. (H) Synchronization of units with click trains. Vector strength computed for different interclick intervals. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test, ****P < 0.0001.