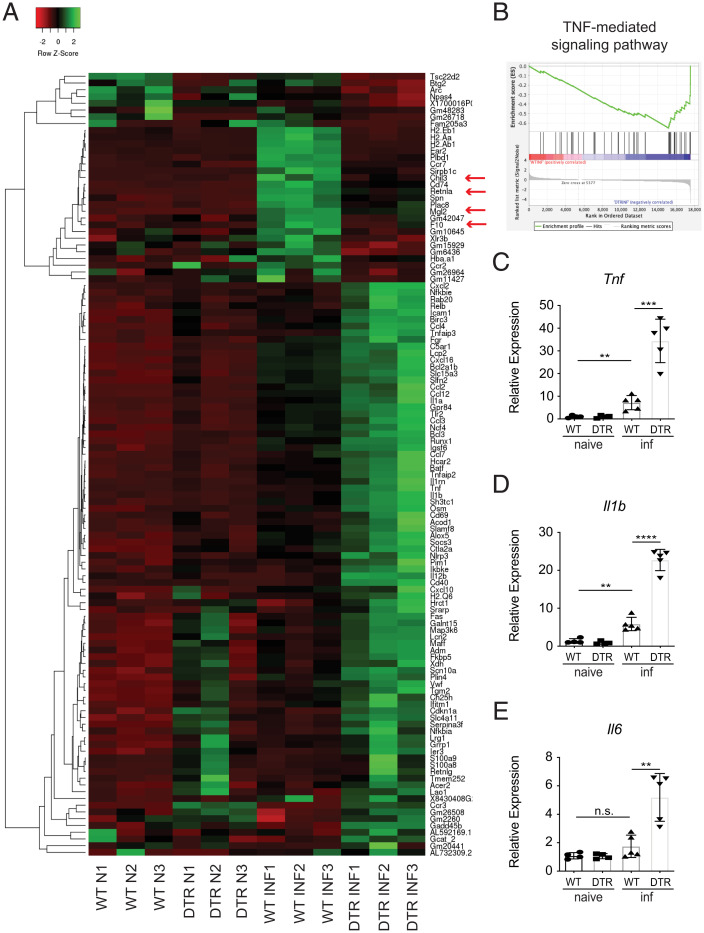
Fig. 3.
Loss of CCR2+ monocytes results in a proinflammatory signature in the brain. WT and CCR2-DTR (DTR) mice were infected with T. spiralis and treated with DT (i.p.) every other day. Mice were sacrificed 8 dpi. (A) Heat map includes genes that are upregulated (FC > 1.5) or downregulated (FC < −1.5) in infected WT versus infected DTR mice and includes three biological replicates per naive group (N) and three biological replicates per infected group (INF). (B) GSEA for TNF-mediated signaling pathway. (C–E) RNA from brain tissue was extracted, and expression of proinflammatory-associated markers was evaluated via RT-qPCR. C–E are representative of at least three independent experiments with at least three biological replicates per group per experiment. Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t test. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; n.s., not significant. Error bars represent ± SD. inf, T. spiralis-infected.