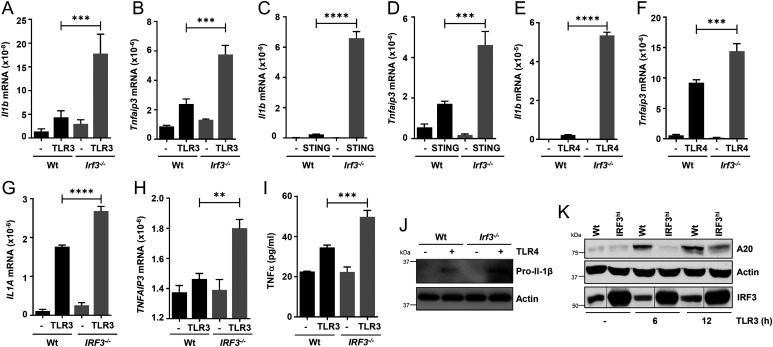
Fig. 4.
IRF3 inhibits inflammatory gene expression in response to nonviral stimuli. (A–F) Wt or Irf3−/− iBMDMs were stimulated with polyI:C (TLR3; A and B), cGAMP (STING; C and D), or LPS (TLR4; E and F) for 4 h, and the mRNAs of Il1b and Tnfaip3 were analyzed by qRT-PCR. (G and H) Wt or IRF3−/− HT1080 cells were stimulated with polyI:C (TLR3; G and H) for 4 h, and the mRNAs of Il1a and Tnfaip3 were analyzed by qRT-PCR. (I) Wt and IRF3−/− (knockout) HT1080 cells were stimulated with polyI:C (TLR3) for 8 h, and the supernatants were analyzed for TNFα by ELISA. (J) Wt or Irf3−/− iBMDMs were treated with LPS (TLR4) for 4 h and analyzed for pro–IL-1β by immunoblot. (K) Wt and IRF3hi HT1080 cells were infected with SeV and analyzed for TNFAIP3/A20 by immunoblot. The results are representative of three experiments; the data represent mean ± SEM. **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001.