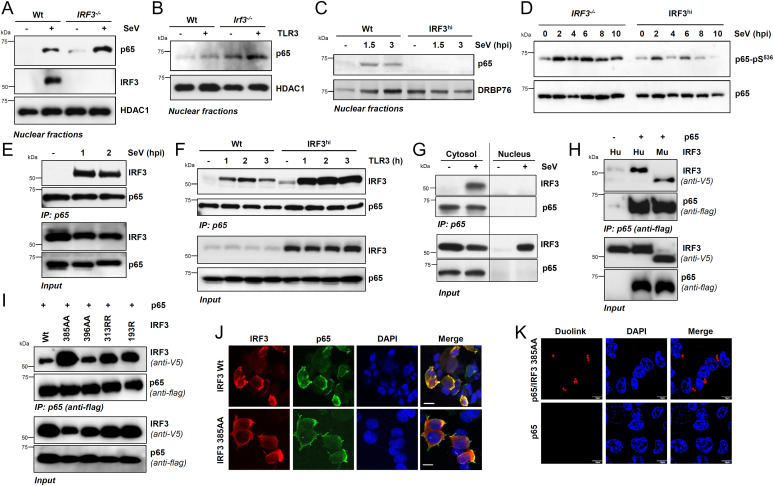
Fig. 5.
IRF3 interacts with NF-κB–p65, independent of transcriptional or RIPA functions, and inhibits NF-κB activation. (A) Wt and IRF3−/− HT1080 cells were either mock-infected or infected with SeV for 2 h when the nuclear fractions were analyzed for NF-κB–p65 and IRF3 by immunoblot. HDAC1 is a marker for nuclear fractions. (B) Wt and Irf3−/− iBMDMs were stimulated with polyI:C (TLR3) for 2 h, when the nuclear fractions were analyzed for NF-κB–p65 by immunoblot. (C) Wt or IRF3hi HT1080 cells were infected with SeV for the indicated time, when the nuclear fractions were analyzed for NF-κB–p65 by immunoblot; DRBP76 is a marker for the nuclear fractions. (D) IRF3−/− and IRF3hi HT1080 cells were infected with SeV for the indicated time, and phospho-p65 (on Ser536) was analyzed by immunoblot. (E) HT1080 cells infected with SeV for the indicated time were subjected to co-IP analyses for the endogenous NF-κB–p65 and IRF3 proteins using ExactaCruz. (F) Wt and IRF3hi HT1080 cells stimulated with polyI:C (TLR3) for the indicated time were subjected to co-IP analyses for NF-κB–p65 and IRF3 proteins, as in E. (G) The cytosolic and nuclear fractions, isolated from the SeV-infected Wt and IRF3hi HT1080 cells, were subjected to co-IP analyses for NF-κB–p65 and IRF3, as in E. (H and I) HEK293T cells, cotransfected with Flag–NF-κB–p65 and V5-IRF3 Wt (H) human (Hu), murine (Mu), or IRF3 mutants (I), as indicated, were infected with SeV for 2 h and subjected to co-IP analyses for the Flag–NF-κB–p65 and V5-IRF3, as indicated. (J) HEK293T cells, cotransfected with NF-κB–p65 and V5-IRF3 Wt or IRF3 385AA mutant, were infected with SeV and immunostained with anti-Flag and anti-V5 antibodies and analyzed by confocal microscopy. (K) HEK293T cells, cotransfected with NF-κB–p65 and V5-IRF3 385AA mutant, were infected with SeV and immunostained with anti-Flag and anti-V5 antibodies, and analyzed by proximal ligation assay. The results are representative of three experiments; the data represent mean ± SEM. Scale bar, 10 µm. IP, immunoprecipitation.