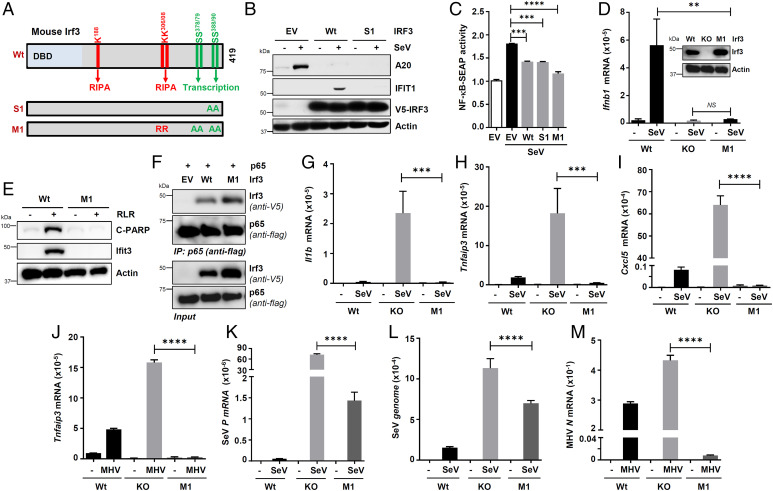
Fig. 7.
IRF3 mutants, active in RIKA but inactive in transcriptional and RIPA, inhibits virus replication and inflammatory gene expression. (A) A cartoon showing mouse Irf3 and its critical residues and domains required for specific functions and the pathway-specific mutants (Irf3-S1 and Irf3-M1). DBD, DNA-binding domain, A, Ala, R, Arg. (B) HT1080/shIRF3 cells, lentivirally expressing Wt or S1 mutant of IRF3, were analyzed for A20 and IFIT1 induction upon SeV infection, by immunoblot 8 h postinfection (hpi). (C) RAW-Blue cells were transfected with Wt or Irf3 mutants (S1 or M1), and the NF-κB–SEAP activity in the culture supernatants was measured upon SeV infection (24 hpi). (D) Wt, Irf3−/−, and Irf3-M1 iBMDMs (Irf3 expression is shown in the inset) were infected with SeV, and Ifnb1 induction was analyzed by qRT-PCR 4 hpi. (E) Wt and Irf3-M1 iBMDMs were transfected with polyI:C for 16 h, when the cell lysates were analyzed for Ifit3 and C-PARP by immunoblot. (F) HEK293T cells, cotransfected with Flag–NF-κB–p65 and V5-Irf3 (Wt or M1), were infected with SeV for 2 h and subjected to co-IP analyses for the Flag–NF-κB–p65 and V5-Irf3. (G–J) Wt, Irf3−/−, and Irf3-M1 iBMDMs were infected with SeV for 4 h (G–I) or MHV for 16 h (J), and the inflammatory target genes were analyzed by qRT-PCR. (K–M) Wt, Irf3−/−, and Irf3-M1 iBMDMs were infected with SeV for 4 h (K and L) or MHV for 16 h (M), and the viral replication was analyzed by qRT-PCR. EV, empty vector. The results are representative of three experiments; the data represent mean ± SEM. IP, immunoprecipitation; KO, knockout, SeV P, SeV P gene, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001.