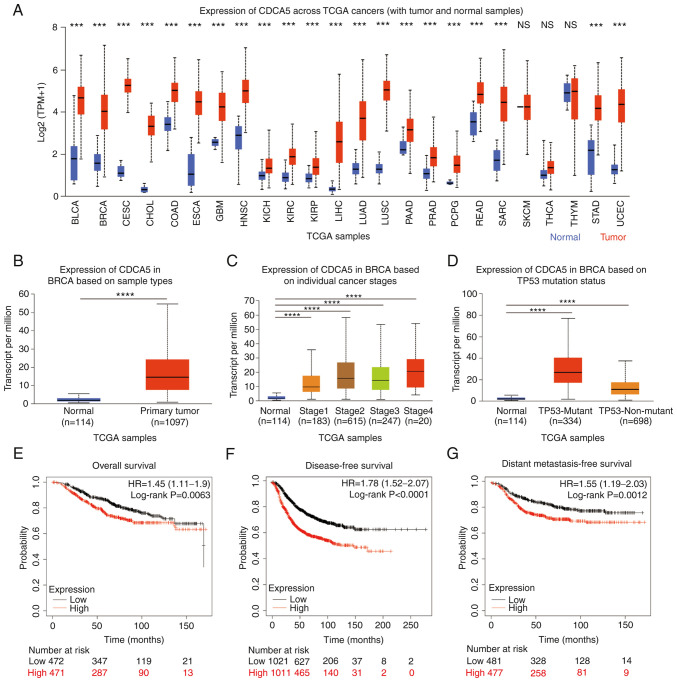
Figure 1.
High CDCA5 expression across TCGA cancers and invasive breast cancer. (A) CDCA5 mRNA expression in various types of cancer compared with normal tissues from the UALCAN database. ***P<0.001. Expression of CDCA5 in BRCA based on (B) sample types, (C) individual cancer stages and (D) TP53 mutation status from TCGA samples. (E) Overall, (F) disease-free and (G) distant metastasis-free survival curves from the Kaplan-Meier Plotter, and the evaluation of the impact of the low (black line) and high (red line) CDCA5 expression. ****P<0.0001. CDCA5, cell division cycle-associated 5; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; BLCA, bladder urothelial carcinoma; BRCA, breast invasive carcinoma; CESC, cervical squamous cell carcinoma and endocervical adenocarcinoma; CHOL, cholangiocarcinoma; COAD, Colon adenocarcinoma; ESCA, Esophageal carcinoma; GBM, glioblastoma; HNSC, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; KICH, kidney chromophobe; KIRC, kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; KIRP, kidney renal papillary cell carcinoma; LIHC, liver hepatocellular carcinoma; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma; LUSC, lung squamous cell carcinoma; PAAD, pancreatic adenocarcinoma; PRAD, prostate adenocarcinoma; PCPG, pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma; READ, rectal adenocarcinoma; SARC, sarcoma; SKCM, skin cutaneous melanoma; THCA, thyroid carcinoma; STAD, stomach adenocarcinoma; UCEC, uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.