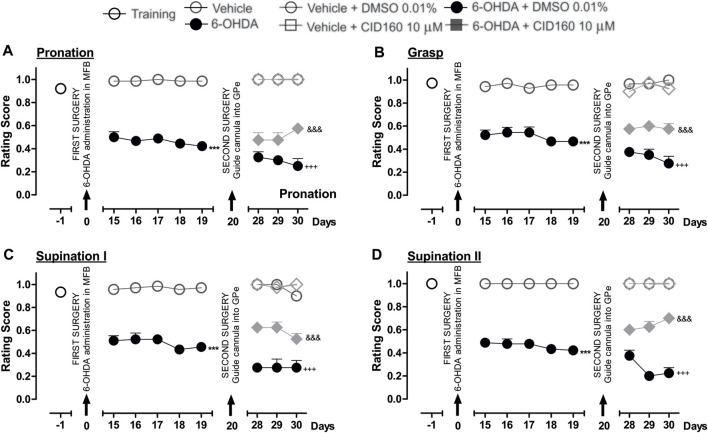
FIGURE 6.
The administration of CID16020046 in the GPe generated superior fine motor skills performance in the hemiparkinsonian rats analyzed in the staircase test. The four movement components selected to evaluate the contralateral forelimb performance for fine motor skills were as follows: (A) Pronation; (B) Grasp; (C) Supination I; and, (D) Supination II. The effect of the intrapallidal administration of CID160 (10 µM) on the movement components were evaluated one day prior to the first stereotaxic surgery (from the 15th to the 19th days post-lesion) and from the 28th to the 30th days post-lesion. It is shown that 6-OHDA + CID160 group performed better in terms of fine motor skills than the 6-OHDA + DMSO group. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM of the fine motor skills scores obtained. *** p < 0.001 vs. vehicle; +++ p < 0.001 vs. vehicle + DMSO 0.01%; &&& p < 0.001 vs. 6-OHDA + DMSO 0.01%; a two-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post-hoc test (n = 5–7/group).