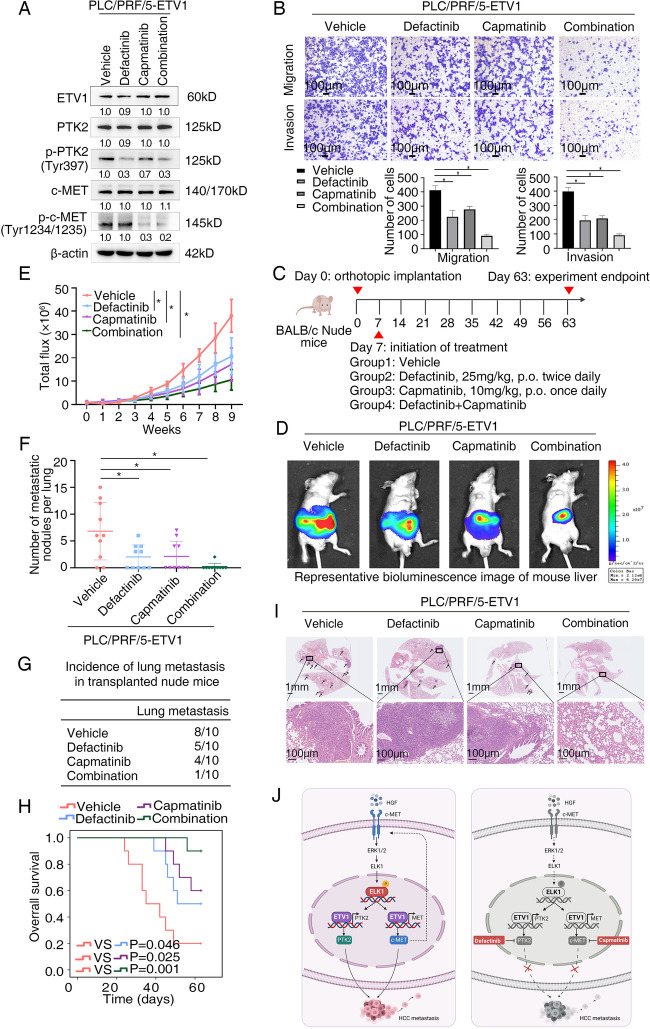
Fig. 8.
The combination of defactinib with capmatinib is effective in reducing ETV1-mediated HCC metastasis (A) The levels of ETV1, p-PTK2 (Tyr397), PTK2, p-c-MET (Tyr1234/1235), c-MET in PLC/PRF/5-ETV1 cells processed with a single agent or the combination of defactinib and capmatinib. (B) HCC cell invasion and migration was evaluated by transwell assay. The combination treatment of defactinib and capmatinib showed the greatest inhibitory effect among all the groups. (C) Schematic diagram of treatment in nude mice of four groups. (Group1: Vehicle, Group2: Defactinib, Group3: Capmatinib, Group4: Defactinib combined with Capmatinib) (D-I) In vivo metastatic assay. (D) The representative BLI images in the liver were shown 9 weeks after implantation with indicated cells. (E) The bioluminescent signals were used to show the growth rate of liver tumors. (F)The number of metastatic lesions in the lung tissues. (G) The occurrence of lung metastasis. (H) The OS of different groups of nude mice. (I) Representative images of H&E staining of lung samples (indicated by arrowheads) from each group. * Represented p < 0.05. All data were displayed as Mean ± SD. (J) Diagram illustrating the mechanisms underlying how ETV1 promotes HCC metastasis and a potential combination strategy. ETV1 mediates HCC metastasis through increasing PTK2 and c-MET expression. HGF upregulates ETV1 expression via c-MET-ERK1/2-ELK1, creating a positive feedback loop that continuously stimulates HCC development. PTK2 inhibition in combination with c-MET inhibition markedly mitigates ETV1-mediated HCC metastasis