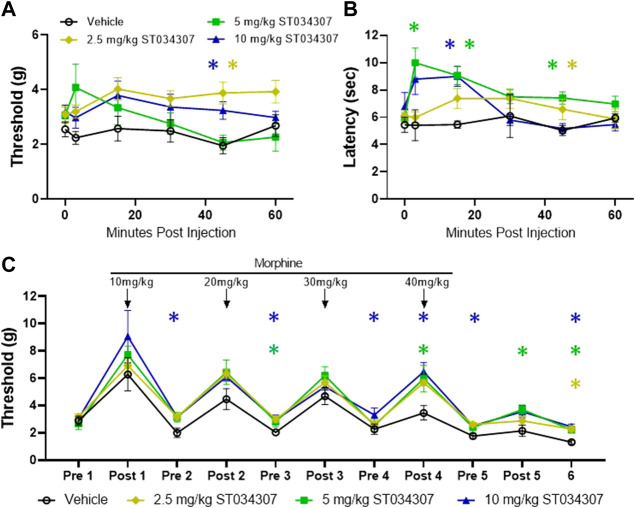
FIGURE 2.
ST034307 produces mechanical and thermal antinociception and attenuates morphine induced hyperalgesia (A) Mechanical paw withdrawal thresholds and thermal latencies (B) between vehicle and ST034307 treated mice. Significant increases in paw thresholds and latencies were seen between vehicle and ST034307 treated mice (repeated measures ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test vs. vehicle, F (3, 31) = 3.691, p = 0.0221 and F (3, 29) = 5.460, p = 0.0042, respectively). (C) To induce escalating morphine tolerance, mice received twice daily injections of morphine (10 mg/kg on day 1 increasing to 40 mg/kg by day 4, sc, 100 uL) along with an injection of either vehicle or ST034307 (2.5–10 mg/kg, ip, 100 uL) 15 min post-morphine. Baseline measurements were measured every morning before morphine injection (Pre) and 30 min post injection (Post) with day 5 and day 6 thresholds measured ∼18 and ∼42 h, respectfully, after last morphine injection (repeated measures ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test vs. vehicle, F (3, 32) = 8.424, p = 0.0003). Asterisk indicates statistical significance at each individual time point (p < 0.05). Data presented as mean ± SEM. Data presented as mean ± SEM with an n = 5 (vehicle) or 10 (2.5–10 mg/kg ST034307)/group.