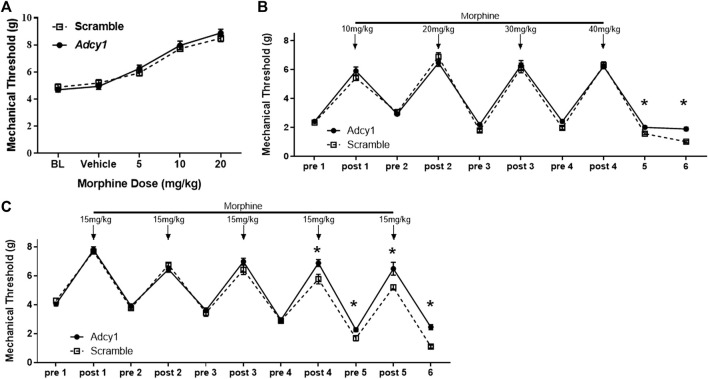
FIGURE 4.
AC1 knockdown via intrathecal delivery of AAV9-Adcy1-shRNA partially attenuates morphine induced hyperalgesia in mice. (A) Knockdown of Adcy1 mRNA does not impact acute morphine antinociception (5–20 mg/kg, sc, measurements taken 30 min after morphine injection). (B) Twice daily escalating injections of morphine (10 mg/kg on day 1 increasing to 40 mg/kg by day 4, sc, 100 µl) induce hyperalgesia that is attenuated in AAV9-Adcy1-shRNA compared to AAV9-Scrambl-shRNA injected mice on Days 5 and 6, ∼18 and ∼42 h after last morphine injection, respectively (repeated measures ANOVA, F (1, 18) = 3.928, p = 0.00630). (C) Morphine tolerance and hyperalgesia established by twice daily injections of morphine for 5 days (15 mg/kg, sc) are reduced in AAV9-Adcy1-shRNA compared to AAV9-Scrambl-shRNA injected mice (F (1, 18) = 17.61, p = 0.0005). Asterisk indicates statistical significance at each individual time point (p < 0.05). Data presented as mean ± SEM with an n = 10/group.