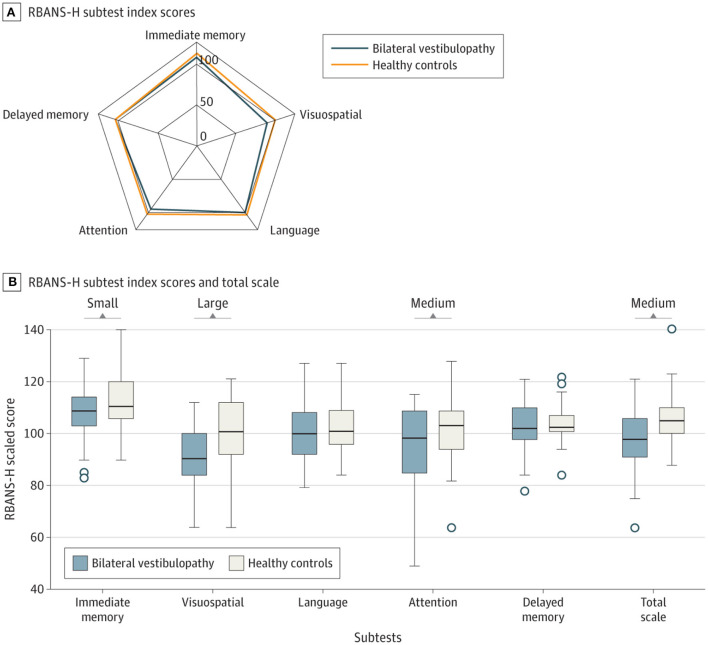
Figure 1.
Effects of bilateral vestibulopathy on the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS-H) scores in different cognitive domains. Comparison of RBANS-H scores between individuals with bilateral vestibulopathy and their matched healthy controls. (A) The relationship between the scores for immediate memory, delayed memory, attention, language and visuospatial function for bilateral vestibulopathy patients and healthy controls. (B) Whiskers indicate range; boxes, interquartile range (IQR); circles indicate outliers; bold line, median d. Small (Cohen's d = 0.2), medium (Cohen's d = 0.5), and large (Cohen's = 0.8) indicate clinically meaningful Cohen's d effect sizes. While there were medium and large differences for attention and visuospatial memory, there were only small effects for immediate memory, language and delayed memory. Reproduced from Bosmans et al. (8).