FIGURE 3.
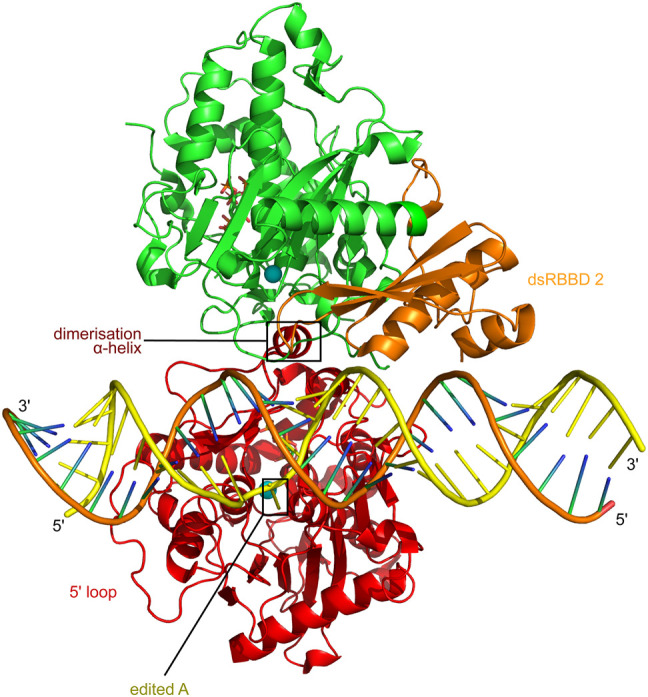
ADAR2 recognizes the editing site as an asymmetric deaminase domain dimer with one positioned dsRBD 2. The ADAR2 catalytic deaminase domain in red is shown behind the dsRNA in this view of the ADAR2 deaminase domain plus dsRBD 2 protein complex with a GLI1 substrate RNA containing 8-azanebularine (8-AZ) at the edited A (Thuy-Boun et al. 2020). The dsRBD 2 of the catalytic deaminase monomer is not resolved in the structure. The adenosine-analog, 8-AN, editing target base, is on the yellow edited strand where the phosphate backbone is slightly kinked, and the 8-AN base is seen flipped back out through the dsRNA minor groove and down towards the blue sphere of the catalytic site zinc atom. A short dimerization helix on the catalytic deaminase domain holds the second, noncatalytic deaminase domain, in green. This second, noncatalytic deaminase domain then positions its associated dsRBDII, shown in orange, for normal dsRBD binding to the dsRNA, without contacting the catalytic deaminase domain.
