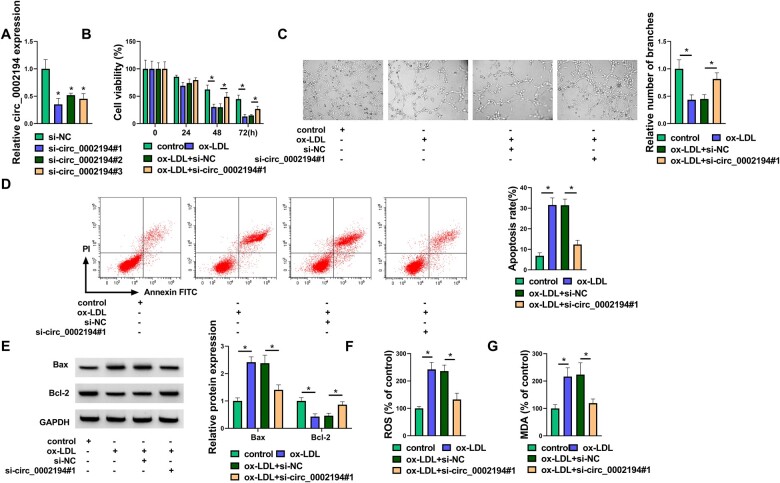
Figure 2:
Silencing circular (circ_0002194 enhanced cell viability and angiogenesis but inhibited apoptotic and oxidative damage in oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. (A) The reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to assess the knockdown efficiency of small interfering (si) RNAs for circ_0002194. (B-G) Human umbilical vein endothelial cells were treated with control, ox-LDL (50 μg/ml), ox-LDL+si-negative controls and ox-LDL+si-circ_0002194#1. (B-C) The Cell Counting Kit-8 assay and the tube formation assay were used to determine cell viability (B) and angiogenesis (C). (D) Flow cytometry was used to measure the cell apoptosis rate. (E) The Western blot was used to detect the protein levels of Bax and Bcl-2. (F-G) (F) Detection of reactive oxygen species and malondialdehyde levels (G) was used to analyse the oxidative injury (P < 0.05). circ: circular; FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate; GAPDH: oxidized low-density lipoprotein; MDA: malondialdehyde; NC: negative control; OX-LDL: oxidized low-density lipoprotein; ROS: reactive oxygen species; si: small interfering.