Figure 5.
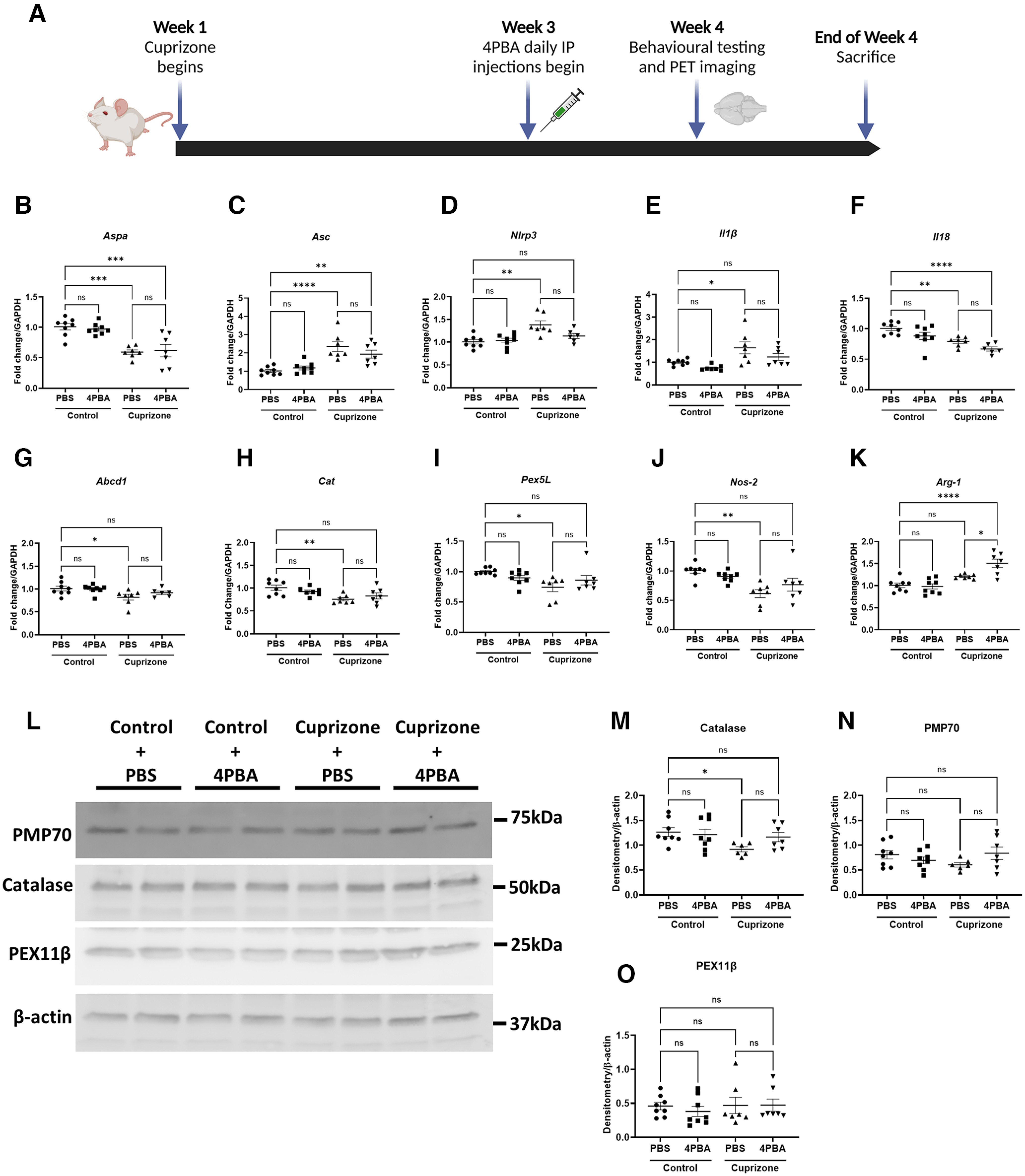
CPZ exposure in mice decreases expression of peroxisome biogenesis and structural genes and increases inflammasome gene expression in the hindbrain. Mice were fed control chow or chow containing 0.265% CPZ for 4 weeks and treated with PBS or 4-PBA (100 mg/kg) intraperitoneally during weeks 3 and 4 of CPZ exposure. Behavioral testing and PET imaging were performed before death at the end of week 4. A, Schematic diagram of mouse treatment regimen created with www.BioRender.com. B–K, Hindbrains of mice (including brainstem and cerebellum) were analyzed by RT-PCR targeting peroxisome and inflammatory genes Aspa (B), Asc (C), Nlrp3 (D), Il1β (E), Il18 (F), Abcd1 (G), Cat (H), Pex5l (I), Nos-2 (J), and Arg-1 (K) (n = 6-8). Error bars represent standard error of the mean. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0005; ****p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test. L–O, Immunoblotting and quantification of peroxisomal proteins catalase (M), PMP70 (N), and PEX11β (O), with representative immunoblot shown (L) (n = 6-8). Error bars represent standard error of the mean. *p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Welch's correction followed by Dunnett's T3 post hoc test).
