Figure 6.
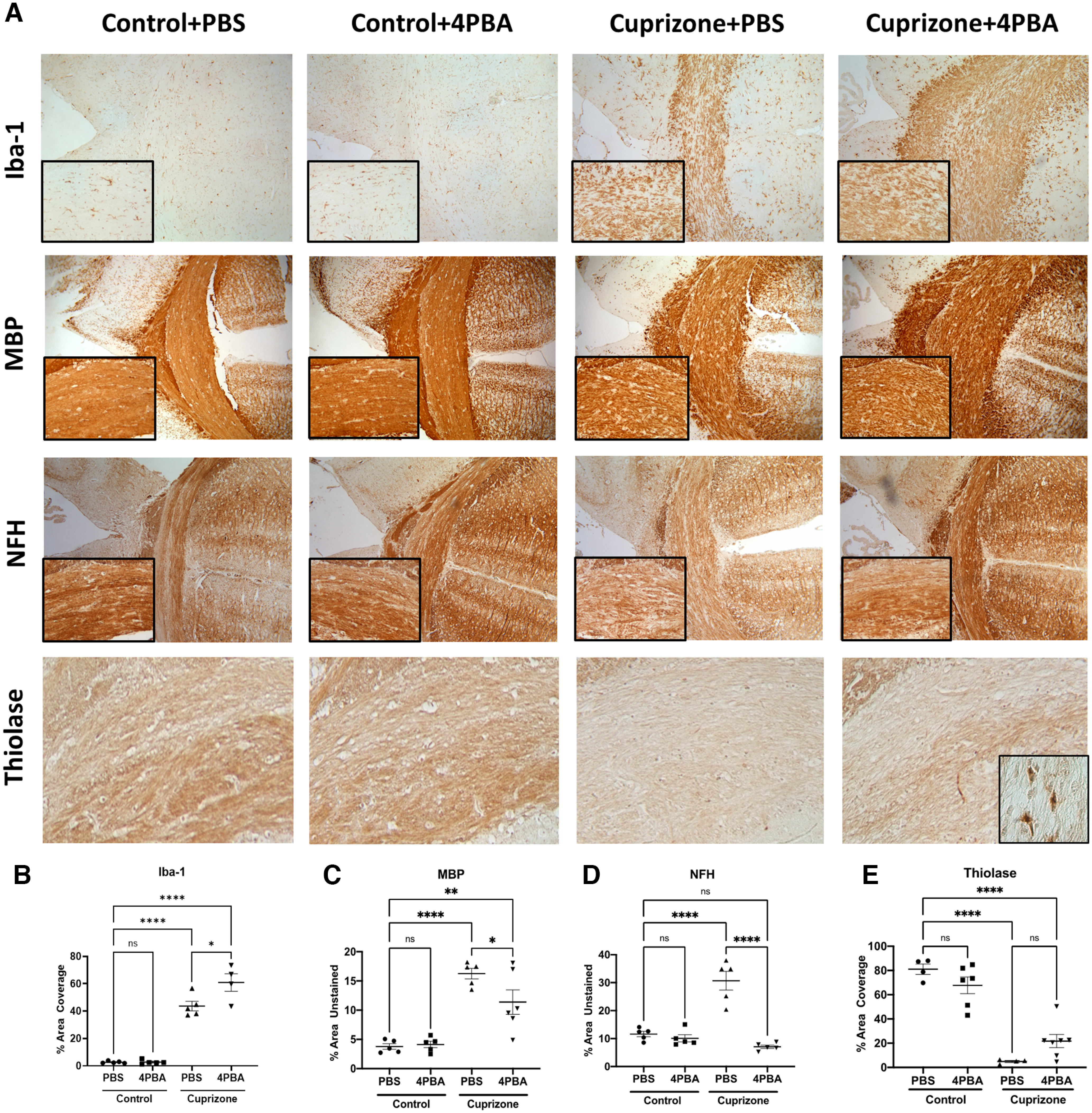
CPZ exposure causes demyelination and axonal injury, while 4-PBA treatment is associated with enhanced CAM recruitment and preserved myelin, axonal, and peroxisomal structure. A–E, Immunohistochemistry of mouse central corpus callosum following CPZ exposure (0.265%) with or without 4-PBA treatment. Representative images (10×) with high-magnification inset (20×) (A) and quantification of Iba-1% area coverage (B), MBP percent unstained area (C), NFH percent unstained area (D), and thiolase percent area coverage (E) of the central corpus callosum. Error bars represent standard error of the mean. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.0005; ****p < 0.0001; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test.
