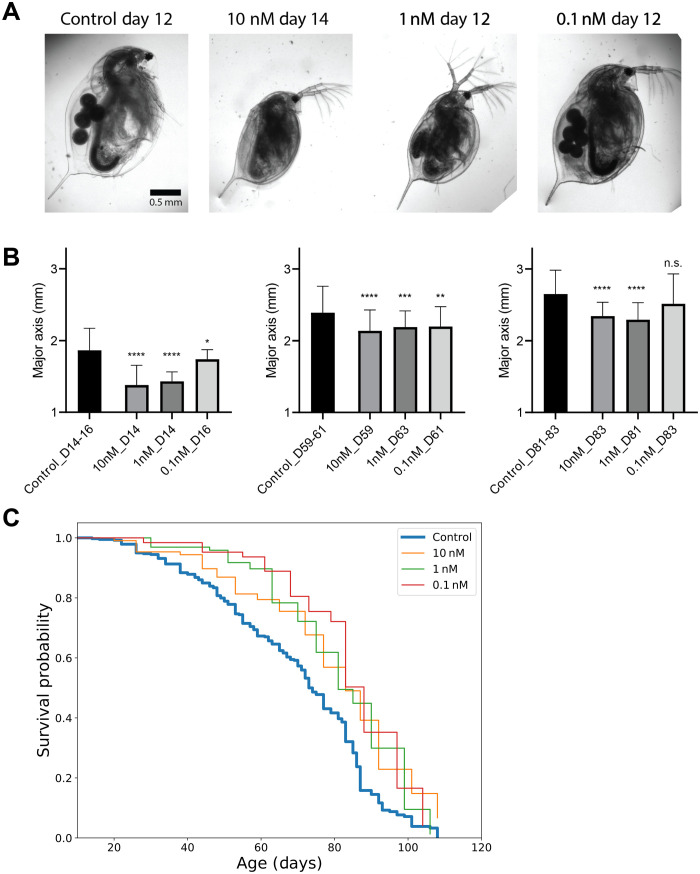
Fig. 5. Rapamycin treatment during development extends life span and reduces the body size of Daphnia magna.
(A) Representative images of D. magna at 12 to 14 days following rapamycin exposure. Also shown is a control animal at the same chronological age. (B) Daphnia body size measurement at days 14 to 16, days 59 to 63, and days 81 to 83. P values are calculated using two-sided Student’s t test. The data are means ± SD. Kruskal-Wallis test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001). n.s., not significant. (C) Survival curves for control and three different concentrations of rapamycin (control, n = 379; 0.01 nM, n = 107; 1 nM, n = 97; and 0.1 nM, n = 63).