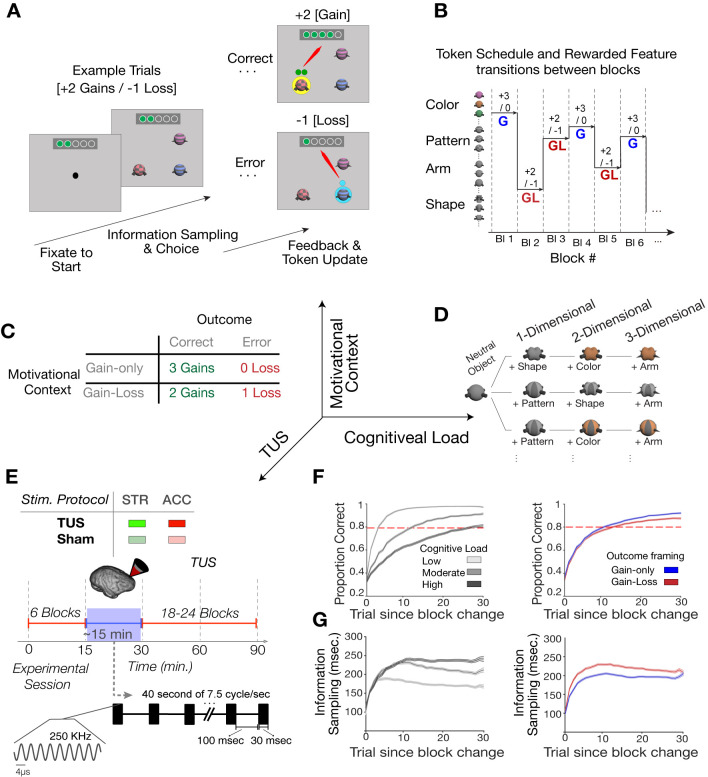
Fig 1. Task paradigm and TUS protocol.
(A) A trial started with central gaze fixation and appearance of 3 objects. Monkeys could then explore objects and choose 1 object by fixating it for 700 ms. A correct choice triggered visual feedback (a yellow halo of the chosen object) and the appearance of green circles (tokens for reward) above the chosen object. The tokens were then animated and traveled to a token bar on the top of the screen. Incorrect choices triggered a blue halo, and in the gain-loss condition 1 blue token was shown that traveled to the token bar where one already attained token was removed. When ≥5 tokens were collected in the token bar, fluid reward was delivered, and the token bar reset to zero. (B) In successive learning blocks, different visual features were associated with reward and blocks alternated randomly between the gain-only (G) and gain-loss (GL) conditions. (C) In the gain-only motivational context, monkeys gained 3 tokens for correct and 0 penalty for each incorrect choice, whereas in the gain-loss context, they gained 2 tokens for each correct and lost 1 token for each incorrect response. The axes (right) show the 3 orthogonal independent variables of the task design (cognitive load, motivational context, and TUS conditions). (D) Cognitive load varied by increasing the number of object features from 1 to 3 and from block to block. (E) In each sonication or sham session, the experiment was paused after 6 learning blocks. There are 4 experimental conditions; TUS in ACC (ACC—TUS; red), or anterior striatum (STR-TUS; green), or sham ACC (ACC-Sham; dimmed red), or sham anterior striatum (STR-Sham; dimmed green); 30-ms bursts of TUS were delivered every 100 ms over a duration of 80 seconds (40 seconds each hemisphere). (F) Proportion of correct choices over trials since block begin for different cognitive loads (left panel; 1–3D, light to dark gray) and motivational contexts (gain-only, blue; gain-loss, red). (G) The average fixation duration on objects prior to choosing an object (information sampling) in the same format as in (F). The lines show the mean and the shaded error bars are SE. Data associated with this plot could be found at: https://figshare.com/projects/TUS_PlosBiology/144330. ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; STR, striatum; TUS, transcranial ultrasound stimulation.