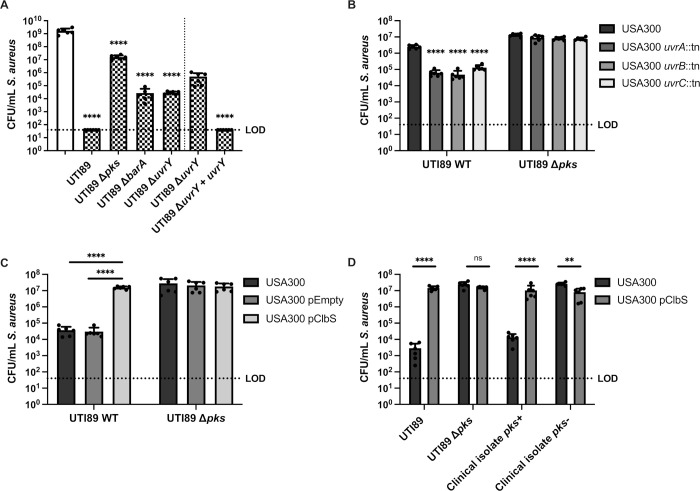
Fig 3. The BarA-UvrY two component system (TCS) and the pks island are required for E. coli-mediated killing of S. aureus.
(A) Enumeration of S. aureus USA300 LAC and mixed (1EC:1SA) macrocolonies with either UTI89 wild type, knockout mutants of the pks island, barA or uvrY or complemented strains. The vertical dotted line indicates that data collected on either side were collected from separate experiments. Data from single species macrocolonies are indicated with open bars, and data from mixed species macrocolonies are indicated with checked bars. N = 6 independent biological experiments. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test for multiple comparison. (B) Enumeration of S. aureus USA300 LAC from 8 h macrocolonies. Wild type S. aureus USA300 LAC and uvrABC transposon mutants were mixed 1EC:1SA with either E. coli UTI89 or knockout mutants of the pks island. N = 6 independent experiments. (C) Enumeration of S. aureus from 24 h macrocolonies. Wild type S. aureus USA300 LAC was transformed with pJC-2343 (pEmpty) or pJC-2343-ClbS (pClbS) and mixed 1:1 with either E. coli UTI89 or knockout mutants of the pks island. N = 6 independent experiments. Individual data points are indicated with closed circles. (D) Enumeration of S. aureus from 24 h macrocolonies. Wild type S. aureus USA300 LAC or USA300 pClbS was mixed 1:1 with either E. coli UTI89, UTI89 Δpks island, pks+ or pks- clinical isolate. N = 6 independent experiments. (B-D) Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons. ****p< 0.0001, error bars represent SD from the mean. All statistical tests were performed on log-transformed CFU data.