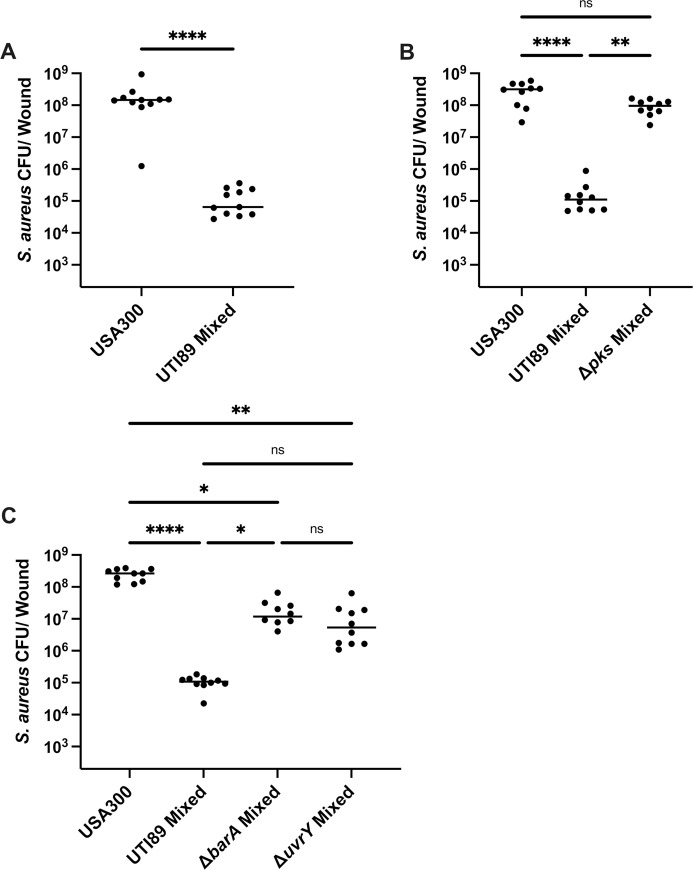
Fig 6. E. coli antagonizes S. aureus growth during wound infection and antagonism is dependent on the pks island and the BarA-UvrY TCS.
Mice were co-infected with E. coli UTI89 and S. aureus USA300 LAC at 1–2 x 106 CFU/wound. Wound CFU were enumerated at 24 h post infection. S. aureus single species infection or co-infection with (A) E. coli UTI89 WT, (B) E. coli pks mutant, or (C) BarA-UvrY TCS mutants. Each black circle represents one mouse, horizontal lines represent the median. N = 2 independent experiments, each with 5–6 mice per group. Statistical analysis was performed using Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-test to correct for multiple comparisons. *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01, ****p< 0.0001. (See S6 Fig for paired E. coli CFU to match the S. aureus data shown here).