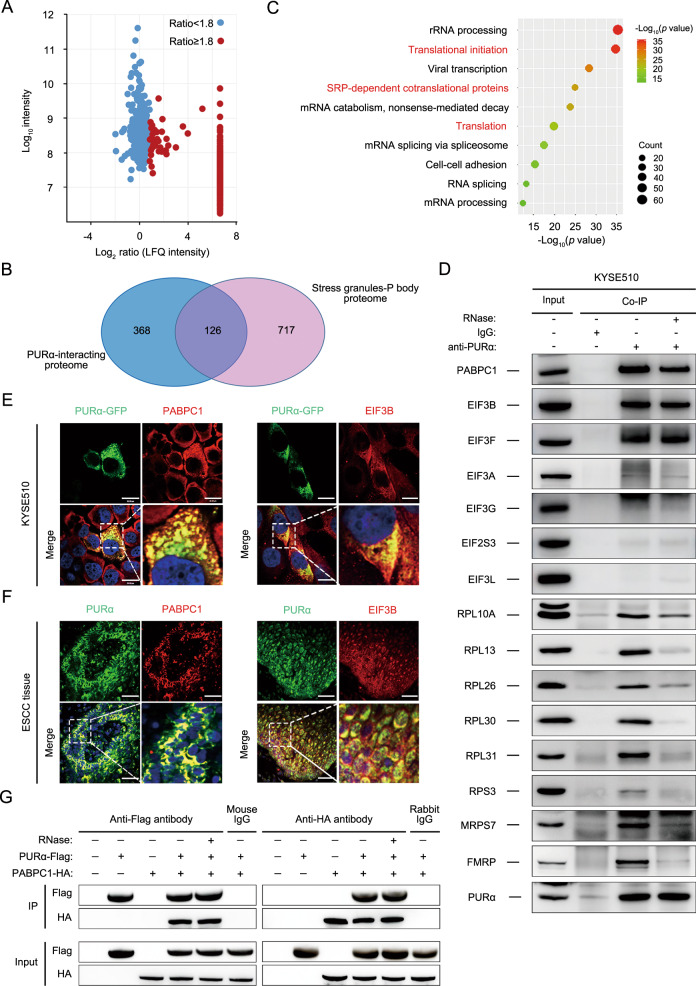
Fig. 4. Cytoplasmic PURα interacts with translation initiation factors directly to regulate protein expression.
A PURα-interacting proteins were identified in KYSE510 cells using a coimmunoprecipitation assay coupled to a label-free quantification (LFQ) proteomic technique. The x-axis indicates the log2-transformed LFQ intensity ratios, and the y-axis indicates the log10-transformed total intensities. The 494 PURα-interacting proteins (red dots) that met the following screening criteria (unique peptides ≥1 and LFQ intensity ratio ≥1.8) are shown. B AVenn diagram between PURα-interacting proteins and the proteome of stress granules and P-bodies was constructed. C GO analysis was implemented with DAVID based on PURα-interacting proteins. The top 10 enriched pathways are shown. D The interaction between PURα and candidate representative proteins associated with mRNA translation was verified by coimmunoprecipitation in KYSE510 cells. E The interaction between PURα and PABPC1 and between PURα and EIF3B was visualized via immunofluorescence staining in KYSE510 cells separately. Scale bars: 30 μm. F The interaction between PURα and PABPC1, and between PURα and EIF3B was visualized via immunofluorescence staining in ESCC tissue separately. Scale bars: 100 μm. G PURα-Flag and PABPC1-HA were overexpressed in 293 cells separately, and the interaction between exogenous PURα and PABPC1 was detected by a coimmunoprecipitation assay.