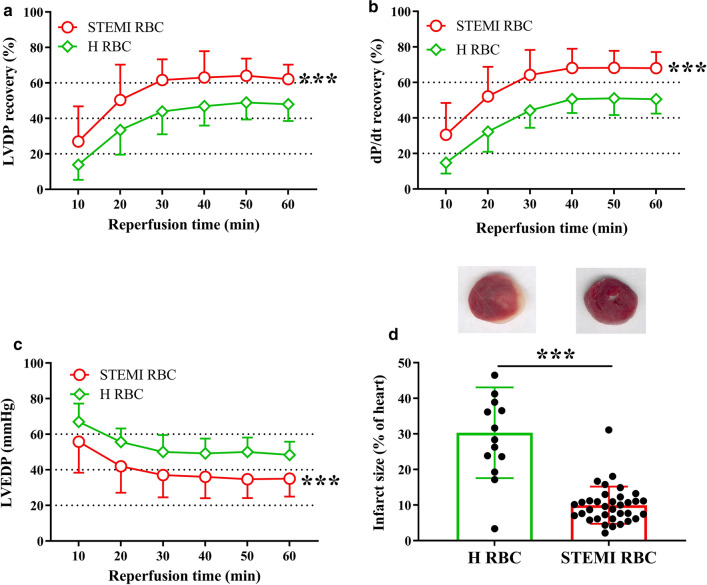
Fig. 1.
Red blood cells (RBCs) from patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) protect the heart from ischemia–reperfusion injury. Effect of RBCs on recovery of cardiac function and infarct size in isolated rat hearts subjected to global ischemia–reperfusion. Recovery of a left-ventricular developed pressure (LVDP), b positive dP/dt, c left-ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP), and d myocardial infarct size of heart following administration of RBCs from patients with STEMI (STEMI RBC) (n = 35) and healthy subjects (H RBC) (n = 23). Post-ischemic LVDP and dP/dt are presented as percentage recovery from baseline and LVEDP in absolute pressure. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical differences in a–c were analyzed with 2-way ANOVA including all time points. Mann–Whitney test was performed in (d). ***P < 0.001 vs. H RBC