Fig. 6.
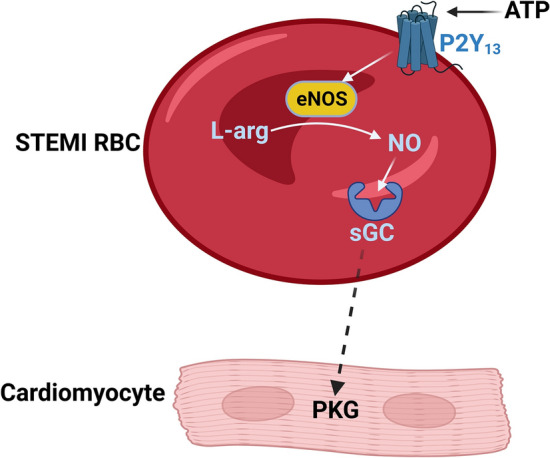
Schematic illustration of the proposed signaling in RBCs from patients with STEMI. RBCs from patients with STEMI induce cardioprotective effects via a mechanism dependent on NOS activation and sGC. Activation of purinergic signaling by ATP via the P2Y13 receptor results in activation of the NO–sGC pathway within the RBCs which leads to the signaling of still unexplored mechanism(s) (dashed arrow) to activate PKG in the cardiomyocytes resulting in cardioprotection. ATP adenosine triphosphate, eNOS endothelial nitric oxide synthase, L-arg L-arginine, NO nitric oxide, PKG protein kinase G, RBCs red blood cells, sGC soluble guanylyl cyclase, STEMI ST-elevation myocardial infarction
