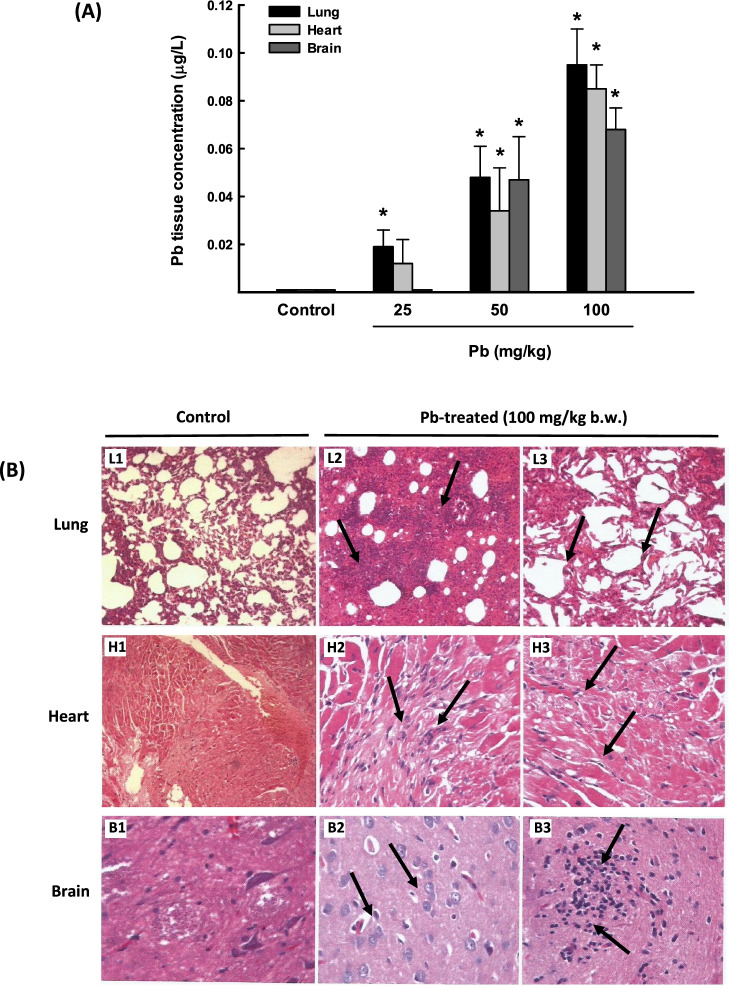
Fig. 1.
Pb distribution and histopathology changes in lung, heart, and brain tissues from rats exposed to once-daily dose of Pb for 3 days. A The Pb concentration levels in lung, heart, and brain tissues from rats treated with Pb (25, 50, and 100 mg/kg b.w.) were determined by ICP-MS. The values are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). *p < 0.05 compared to the control (Pb 0 mg/kg b.w.). B Histopathologic examination of rat lung, heart, and brain tissues from rats treated with Pb (100 mg/kg Pb b.w.) was performed using H&E staining. Representative images of lung histology of control rat (L1) show a normal architecture (50× magnification), whereas L2 (100× magnification) and L3 (200× magnification) show severe interstitial inflammation, fibrosis, and alveolar collapse in the lungs. H1 shows a normal heart (20× magnification), whereas H2 and H3 show marked congestion, interstitial inflammation, fibrosis, and focal cardiac muscle degeneration (100× magnification). B1 represents normal brain structure (200× magnification) and B2 (200× magnification) and B3 (100× magnification) demonstrate cellular degeneration and increased inflammatory cells