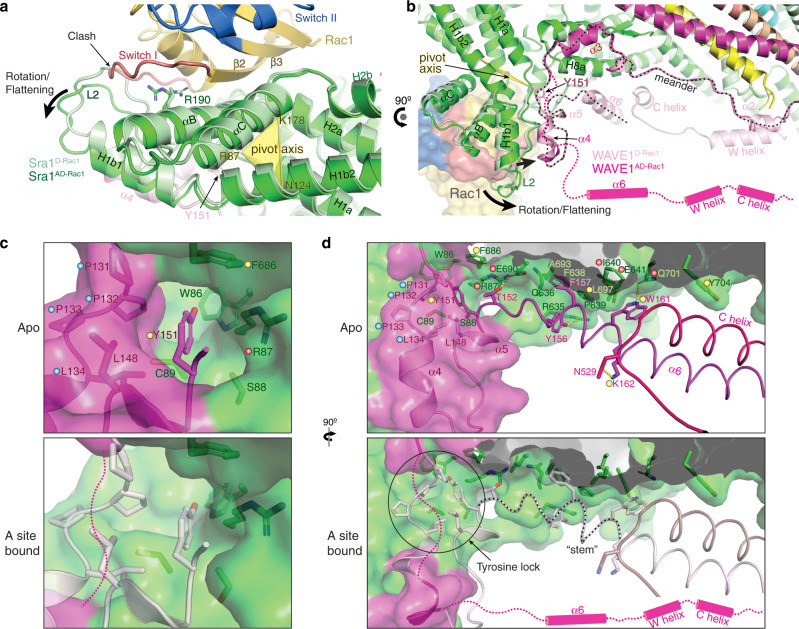
Fig. 4. Rac1 binding to the A site drives a conformational change to release WCA.
a, b Overlay of WRCAD-Rac1 (dark colors) and WRCD-Rac1 (light colors) structures showing conformational changes of the A site upon Rac1 binding. Sequences of which the densities are not observed in WRCAD-Rac1 structure, but are present in WRCD-Rac1 are indicated by magenta dashed lines and cylinders. The meander region in WAVE1 is traced by the black dotted line. c, d Comparison of the tyrosine lock and “stem” (traced by the black dotted line) region before and after Rac1 binding to the A site. Structures in light colors are from the unbound state in WRCD-Rac1 and used as reference point for the A-site bound state. Residues critical for stabilizing the tyrosine lock and “stem” components are labeled and shown in sticks. Dots of different colors indicate residues of which mutations were involved in human disease (red), previously designed and shown to disrupt WRC inhibition (yellow), or newly introduced in this work (blue).