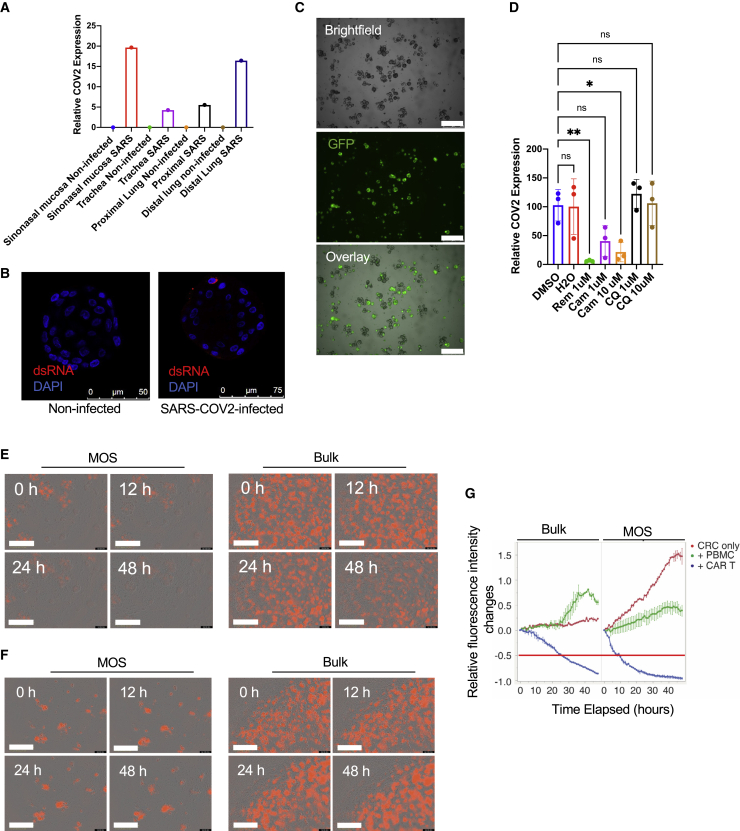
Figure 4.
MOS-based assays for viral infections and assessing CAR-T cell-mediated cytotoxicity
(A) qRT-PCR measures the SARS-CoV-2 expression in the airway MOSs after 48 h of infection.
(B) Representative images of double-strand RNA (dsRNA) immunofluorescence (IF) staining of non-infected and SARS-CoV-2-infected airway MOSs.
(C) Representative images of airway MOSs after influenza infection for 24 h. GFP-positive spots indicate the influenza-infected MOSs (scale bar: 500 μm).
(D) qRT-PCR measures the SARS-CoV-2 expression in sinonasal MOSs in response to the treatments of remdesivir, camostat, or CQ. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ns, not significant (bars show the mean ± SEM of n = 3 biological replicates). One-way ANOVA was used to determine the statistical significance.
(E) Representative images from co-culture of HER2+ CRC MOSs (left) or bulk organoids (right) with anti-HER2 CAR-T cells over a 48 h period (scale bar: 500 μm).
(F) Representative images from co-culture of HER2+ CRC MOSs (left) or bulk organoids (right) with PBMCs over a 48 h period (scale bar: 500 μm).
(G) Time-course data from IncuCyte S3 for red fluorescent signal with bulk organoid comparison. The red horizontal line indicates the 50% decrease of red fluorescence intensities compared with time 0.