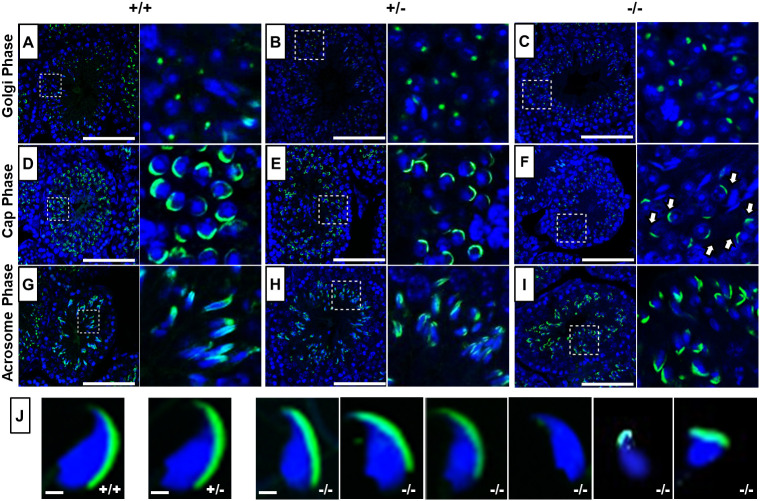
Fig. 5.
Acrosome analysis using PNA-FITC fluorescence staining. (A-I) Immunofluorescence staining for acrosome biogenesis on testes sections and mature sperm of WT, Pfn4+/− and Pfn4−/− mice (n=3 biological replicates/genotype). In the Golgi phase, the proacrosomal granule (green) was labeled by PNA-FITC in WT (A), Pfn4+/− (B) and Pfn4−/− (C) round spermatozoa. In the cap phase, acrosomal caps (green) were stained in WT (D), Pfn4+/− (E) and Pfn4−/− (F) round spermatozoa (white arrows show abnormal cap structures). In the acrosomal phase, PNA-FITC-labeled the acrosomal area in WT (G), Pfn4+/− (H) and Pfn4−/− (I) elongated spermatids. Dashed boxes indicate the areas enlarged to the right. (J) Immunofluorescence staining using PNA-FITC (green) on epididymal sperm cells of WT, Pfn4+/− and Pfn4−/− mice (n=3/genotype) to show the variety of Pfn4−/− sperm such as malformed acrosome and abnormal head morphology. Scale bars: 20 μm.