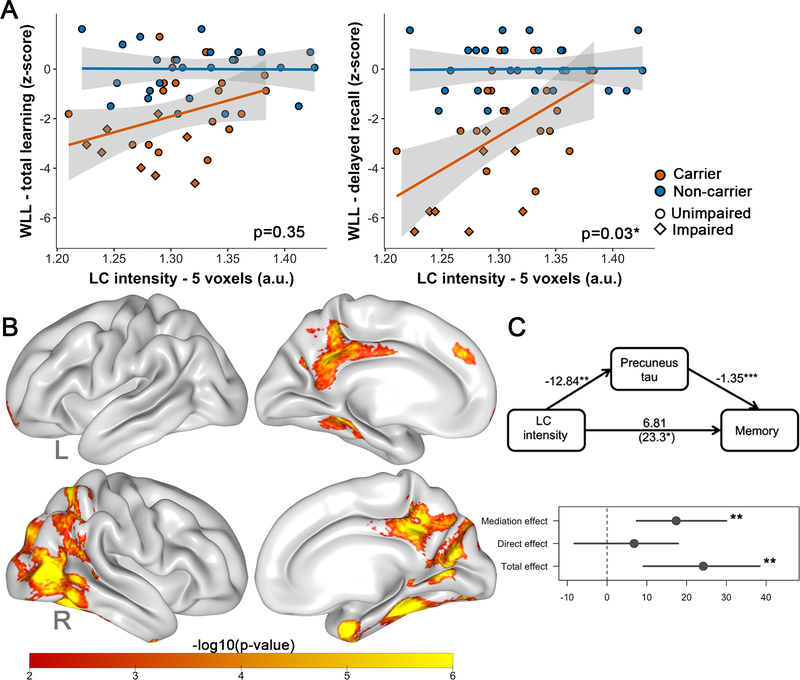
Figure 4: Associations between LC intensityr and memory performance.
Note: A) Differences between carriers (n=26) and noncarriers (n=27) in the association between LC intensityr and memory (left: learning, right: delayed recall). Shaded regions show the 95% confidence interval. B) Quasi-Bayesian Monte Carlo Mediation results: vertex-wise analyses showing which tau regions (FTP SUVr, PVC) mediated the relationship between LC intensityr and memory in the carriers (n=26). Analyses were corrected for multiple comparisons using a cluster-wise correction at p<0.01. The scale bar reflects the magnitude of the probability of the indirect (mediation) effect (expressed in -log10(p-value); yellow: greater; red: smaller). C) ROI-based analyses (precuneus) confirming that precuneus FTP (SUVr, PVC) mediates the relationship between LC intensityr and memory. Abbreviations: WLL= word list learning, L=left, R=right