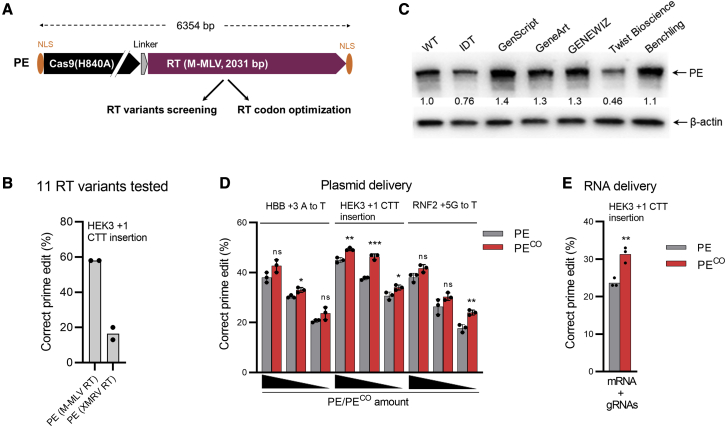
Figure 1.
RT variant screening and codon optimization
(A) Schematic of the PE gene cassette employed in this study. PE consists of Cas9-nickase (Cas9 [H840A]) and M-MLV RT. The bipartite SV40 nuclear localization signals (bpNLSs) are marked in orange and a linker in gray. (B) Screening of prime editing activity of 11 RT variants codon optimized by GenScript showed activity only for XMRV RT is shown (all variant data shown in Figure S1). PE constructs were transfected with plasmids encoding pegRNA and ngRNA into HEK293T cells, and prime editing results were analyzed after 3 days. (C) The effect of RT codon optimization on PE expression using algorithms from different companies is shown. Same amounts of PE plasmids were transfected into HEK293T cells, and western blotting was conducted after 3 days. PE protein expression levels were normalized to β-actin protein levels, and wild-type (WT) PE protein expression level was arbitrarily set to 1.0 (indicated below the PE blot). The image shows a representative blot from two independent experiments with similar results. (D) Comparison of prime editing frequencies of the original PE and the codon-optimized PECO by plasmid delivery is shown. HEK293T cells were transfected with varying amounts of PE or PECO (1,500, 300, and 60 ng) together with fixed amounts of plasmid encoding pegRNA and ngRNA. After 3 days, PCR products were subjected to Sanger sequencing and ICE analysis to evaluate prime editing frequencies. (E) Comparison of prime editing frequencies of PE and PECO by all-RNA delivery is shown. PE mRNA and synthetic pegRNA and ngRNA were electroporated into HEK293T cells. Cells were subjected to ICE analysis 3 days post-transfection. Bars represent mean values ± SD, and all data points for individual replicates are shown. ns, not significant; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.