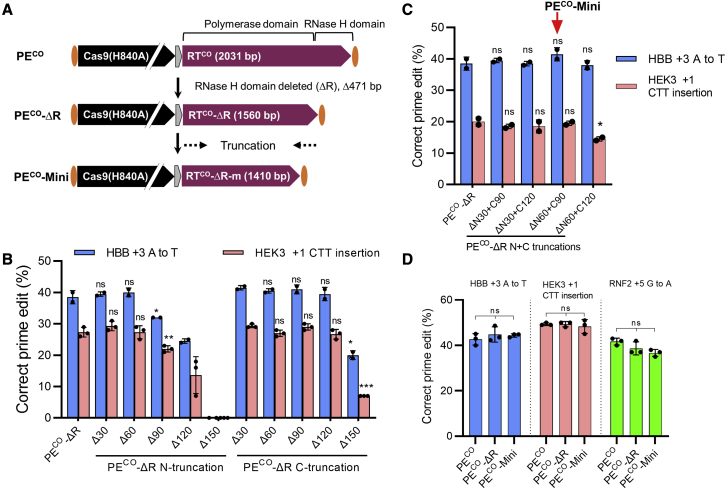
Figure 2.
Generation of a minimal PE by truncating M-MLV RT
(A) Schematic of PECO and truncated PECO variants used in this study. The RT is composed of a polymerase and an RNase H domain. Initially, a truncated PE was made with the RNase H domain deleted (471 bp) to form PECO-ΔR. Subsequently, serial 30-bp truncations at both ends were tested with the aim of generating a minimal PECO (PECO-Mini). (B) Minimizing M-MLV RT by deleting the RNase H domain (PECO-ΔR) and by further N- and C-terminal trimming is shown. The same molar amounts of PECO-ΔR and trimmed PECO-ΔR plasmids were transfected into HEK293T cells together with fixed amounts of plasmids encoding pegRNA and ngRNA. Cells were subjected to ICE analysis for evaluating prime editing activity 3 days post-transfection. (C) Combinatorial N- and C-terminal truncations were analyzed for prime editing efficiencies as in (B). Based on the activity, we selected RT-ΔR with ΔN60 + C90 as the minimal RT, which is 1,410 bp long. (D) Comparison of PECO and the two truncated variants PECO-ΔR and PECO-Mini performed as in (B) is shown. Bars represent mean values ± SD with all data points from independent experiments shown. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.