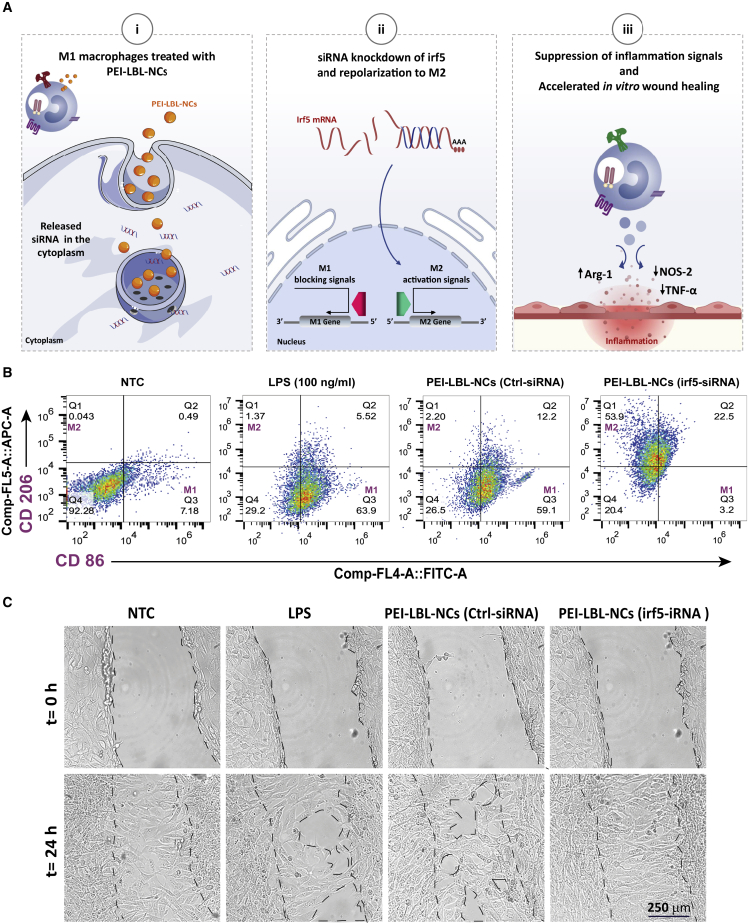
Figure 7.
Enforced M1-to-M2 macrophage repolarization using siIRF5-loaded polyethyleneimine (PEI) layer-by-layer (LBL) nanocomplexes (NCs)
(A) i: M1 macrophage treated by IRF5 siRNA loaded in PEI LBL (NCs. ii: reprogramming into a pro-healing phenotype by successful release of IRF5 siRNA in the cytoplasm. iii: macrophage phenotype change from the M1 to the M2 phenotype leads to faster wound healing in an in vitro scratch assay. (B) Representative flow cytometry results showing the CD206+ (M2 marker) and CD86+ (M1 marker) populations in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells after treatment with PEI LBL NCs loaded with IFR5 siRNA or Ctrl (control) siRNA. (C) For the in vitro wound healing assay, the proliferation of NIH-3T3 fibroblasts was monitored by transmission microscopy after treatment with conditioned cell culture medium (C-CCM) containing secreted factors from macrophage cells (RAW 264.7) stimulated with LPS and treated with PEI LBL NCs loaded with IRF5-siRNA or Ctrl siRNA. Transmission microscopy images show NIH 3T3cells before (0 h) and 24 h after treatment with C-CCM from LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells treated with PEI LBL NCs loaded with IRF5 siRNA or Ctrl siRNA, NTC, non-treated control. Adapted from Sharifiaghdam et al.138