Figure 1.
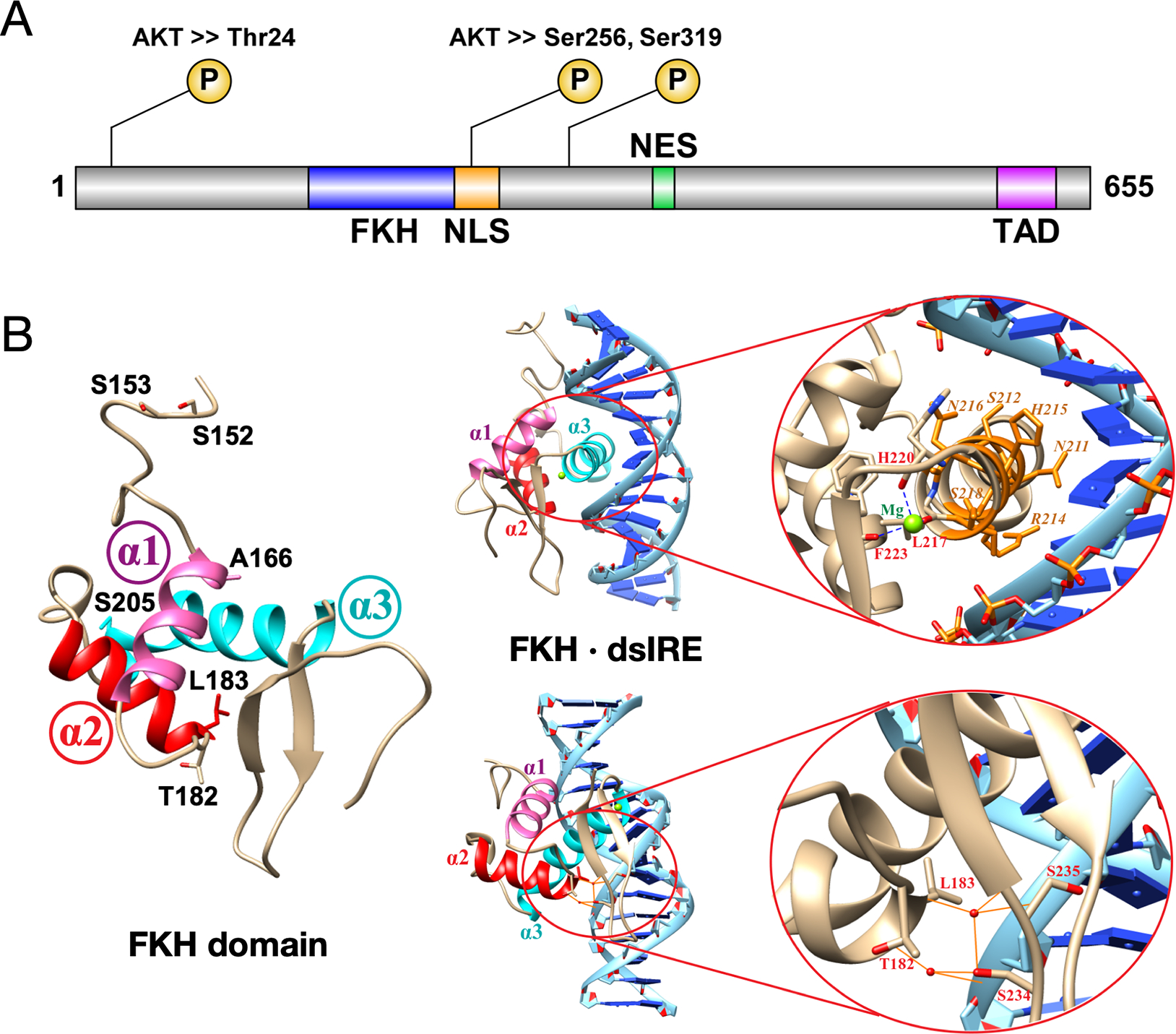
(A) FOXO1 functional domains are shown with three AKT-mediated phosphorylation sites for inactivation. FKH is forkhead DNA-binding domain; NLS is nuclear localization sequence/signal; NES is nuclear export sequence/signal; TAD is transactivation domain. (B) The FKH domain (PDB 3COA) has three helices labeled α1 (pink), α2 (red) and α3 (cyan). The six residues where all eight mutations are found are labeled; none are located in helix α3, which makes contacts with binding sequence IRE. Residues T182, L183, S234 and S235 make key hydrogen bonds with the DNA phosphate backbone, mediated by water molecules (red spheres).
