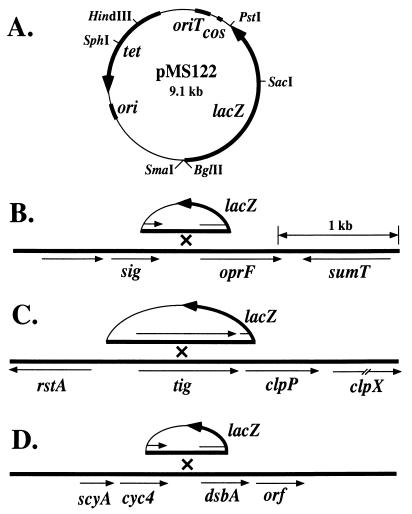
FIG. 2.
Strategy for the analysis of the transcriptional regulation of oprF and dsbA, which encode proteins enhanced by mucA22, and of clpP, which was constitutive. (A) Map of the lacZ transcriptional fusion vector pMS122 used to construct integrative lacZ gene fusions in P. aeruginosa PAO1 and PDO300. Genes indicated are lacZ (β-galactosidase), cos (cohesive ends of lambda), oriT (origin of transfer from RK2), tet (tetracycline resistance), and ori (the ColE1 origin of replication). Below are shown the genes flanking oprF, clpP, and dsbA, which were obtained from the genomic sequence analysis (35) of strain PAO1. (B) Depiction of a fragment in pMS122 containing the 5′ end of oprF integrated into the chromosome by homologous recombination to generate an oprF-lacZ fusion. sig encodes an ECF sigma factor, and sumT encodes a homologue of a uroporphyrin biosynthetic enzyme in P. fluorescens. (C) Depiction of a fragment in pMS122 containing the 5′ end of clpP integrated into the chromosome by homologous recombination to generate a clpP-lacZ fusion. rstA encodes a transcriptional regulatory protein in E. coli, and clpP and clpX encode homologues of proteases in E. coli. (D) Depiction of a fragment in pMS122 containing the 5′ of dsbA integrated into the chromosome by homologous recombination to generate a dsbA-lacZ fusion. scyA encodes a homologue of the mono-heme c-type cytochrome in Shewnaella putrefaciens, cyc4 encodes cytochrome c4, and orf is an open reading frame that encodes a protein of unknown function.