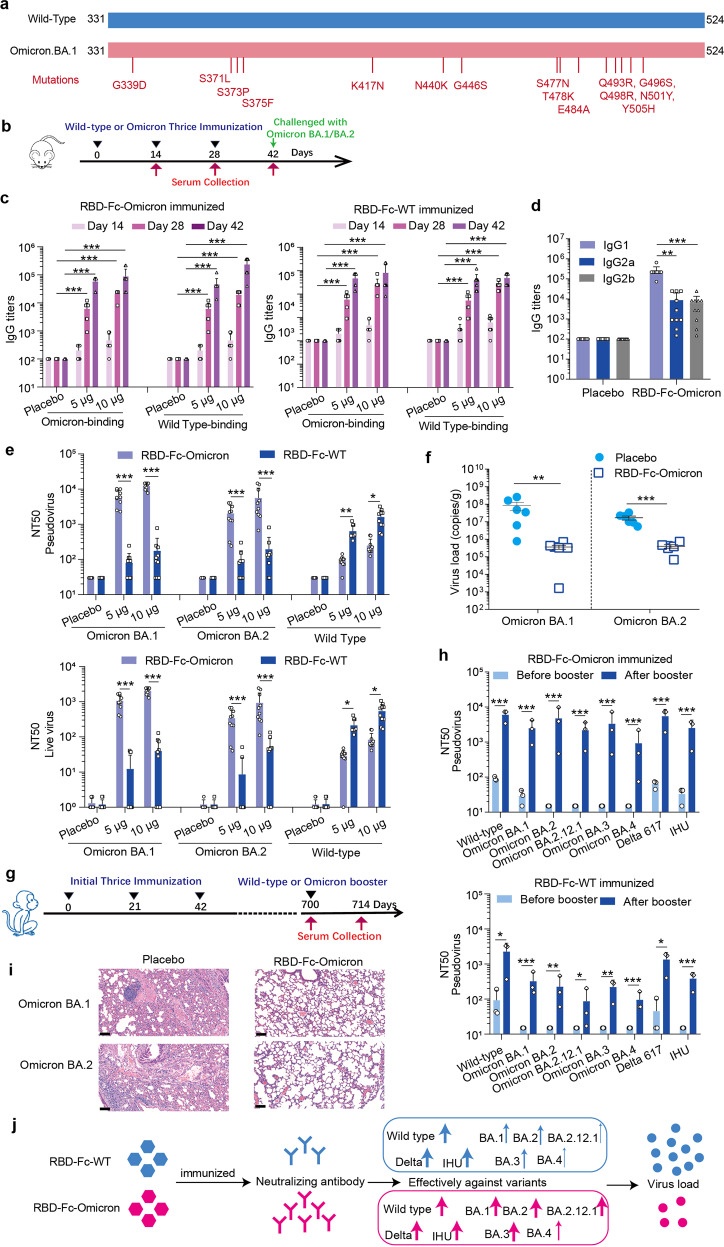
Fig. 1.
Development and characterization of an updated RBD-Fc fusion protein vaccine against Omicron. a Vaccine design, Structural model of amino acid mutations in the RBD of Omicron BA.1 variant of SARS-CoV-2. All mutations in the RBD were shown. b The immune program of RBD-Fc-Omicron and RBD-Fc-WT in mice. Groups of female BALB/c mice (n = 9-10) were immunized intramuscularly with three doses of 5 μg or 10 μg of RBD-Fc-Omicron at 14-day interval. Sera were collected on day 14, day 28, and 42 after the first immunization. The IgG titers (c), antibody isotype (d), and the NT50 (e) were analyzed. To test the protective effect of RBD-Fc-omicron, BALB/c mice were immunized with RBD-Fc-Omicron Vacc (10 μg/mouse) on day 0, day 14, and day 28. Two weeks after the last immunization, mice were inoculated with Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 intranasally (n = 6, 3 × 103 TCID50/mouse), On day 3 post-infection, six mice in each group were sacrificed and harvest. f RT–qPCR was used to measure total viral genome copies in lung tissues. i Histopathological changes in lung tissues observed by light microscopy using haematoxylin and eosin staining (Scale Bar: 100 μm). g The immune program of RBD-Fc-Omicron and RBD-Fc-WT in macaques. Groups of macaques were intramuscularly immunized and boosted with 10 μg vaccines (n = 3), and sera were detected on day 700 and day 714 after the first immunization. h Neutralizing titers after a homologous or heterologous booster RBD-Fc fusion protein vaccine in macaques. j The pattern diagram of our study. The update Omicron vaccine has the immunodominance against VOCs. All data are shown as means ± SD, and a one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons tests or t-test is used (*P <0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)